Introduction

"Arctic Active Cooling. Endless Possibilities. We capture new technologies in mobile and compact cooling. Full-size cooling in a miniature design, customized to make your device stand out with innovative thermal management."
In the realm of modern refrigeration, water-cooled condensers play a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency and performance. These systems utilize water as a cooling medium, providing a reliable alternative to traditional air-cooled units. By understanding how these refrigeration condensers operate, we can appreciate their significance in various applications, from industrial cooling to commercial air conditioning.
Understanding Water-Cooled Condensers
A water-cooled condenser is essentially a heat exchanger that uses water to remove heat from refrigerants circulating within the system. Unlike air-cooled condensers that rely on ambient air for cooling, the condenser and coil in a water-cooled setup are designed to maximize thermal exchange through liquid circulation. This technology not only improves efficiency but also contributes to quieter operation and reduced energy consumption.
Importance in Refrigeration Systems
Water-cooled refrigeration systems are indispensable in many industries due to their superior performance and reliability. They excel in large-scale applications where space is at a premium or where high cooling capacities are required, such as data centers or manufacturing plants. The integration of water-cooled chillers allows for more compact designs while delivering consistent temperature control across various processes.
Key Components of a Water-Cooled Condenser
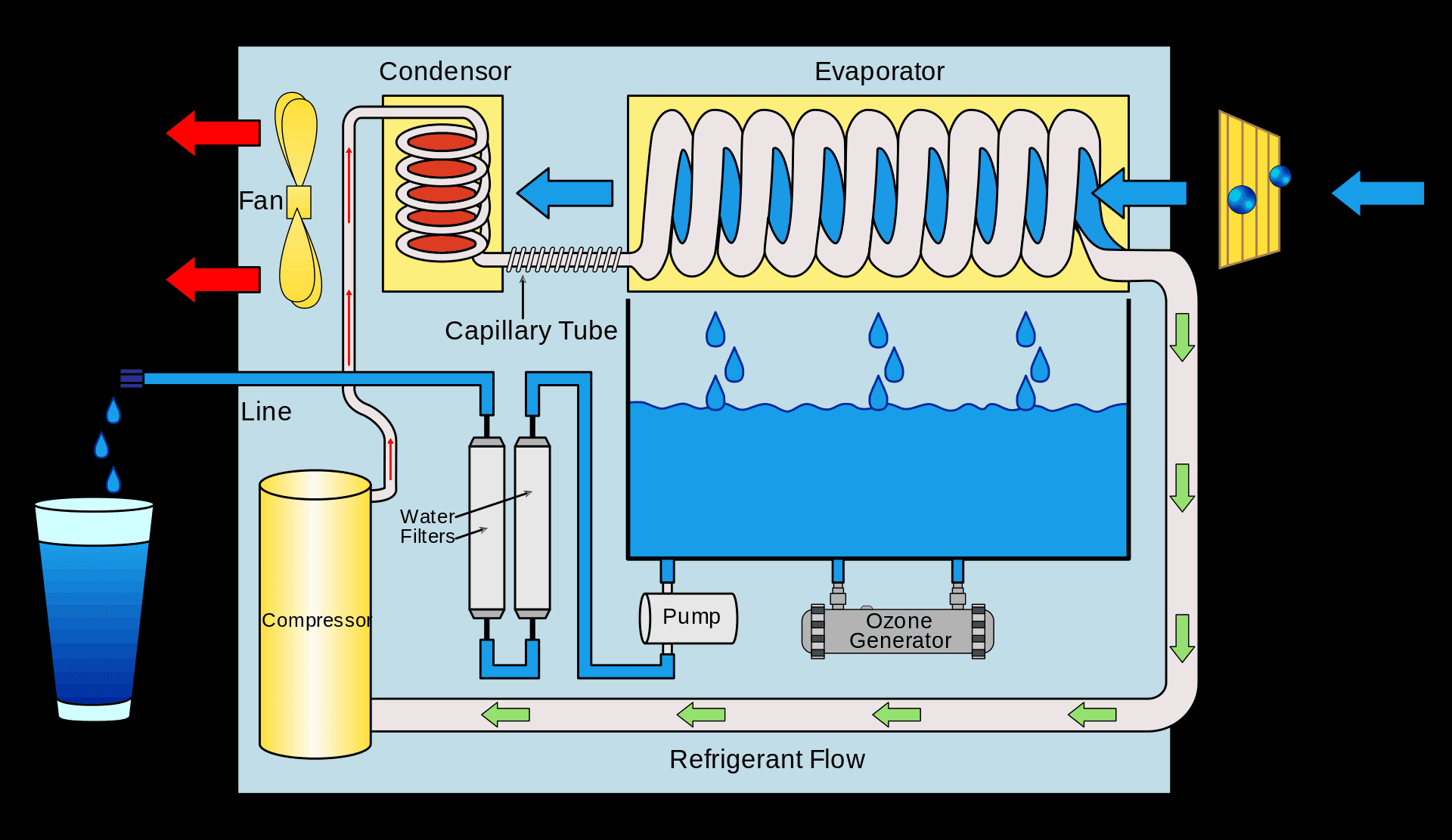
Understanding the key components of a water-cooled condenser is essential for grasping its functionality. At the heart of this system lies the refrigeration condenser coil, which facilitates heat transfer between refrigerant and circulating water. Other vital elements include pumps for circulating chilled water, valves for regulating flow, and control systems that ensure optimal operation throughout varying conditions.
What is a Water-Cooled Condenser?
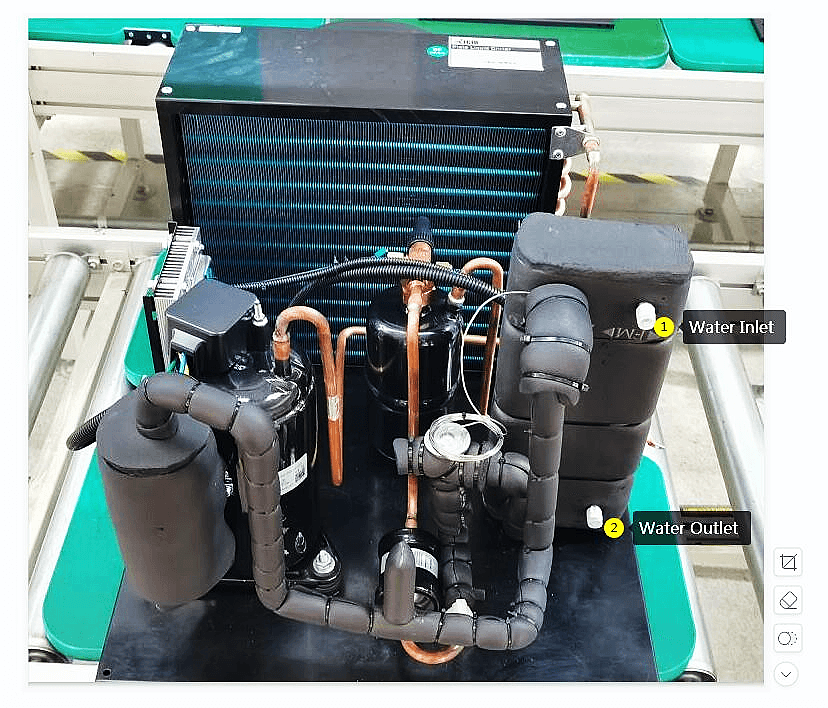
Water-cooled condensers are essential components in many refrigeration systems, designed to efficiently remove heat from refrigerants. By utilizing water as a cooling medium, these condensers ensure that the refrigeration condenser coil operates optimally, maintaining the desired temperature for various applications. Their effectiveness makes them a preferred choice in both commercial and industrial settings.
Definition and Purpose
A water-cooled condenser is a type of heat exchanger that uses water to condense refrigerant vapor back into liquid form after it has absorbed heat from the environment. The primary purpose of this device is to facilitate efficient heat transfer, ensuring that the refrigeration system operates smoothly and effectively. In essence, this condenser plays a critical role in maintaining the overall efficiency of water cooled refrigeration systems.
Comparison with Air-Cooled Systems
When comparing water-cooled systems with air-cooled systems, several key differences emerge. Water-cooled condensers typically offer enhanced efficiency since they can dissipate heat more effectively than air-cooled counterparts, especially in high-load conditions. Additionally, while air-cooled units depend on ambient air temperatures for cooling, water cooled chillers can maintain consistent performance regardless of external weather conditions.
Applications in Various Industries
Water-cooled condensers find applications across numerous industries due to their reliability and efficiency. From large-scale manufacturing facilities requiring robust refrigeration solutions to commercial buildings utilizing chillers for HVAC systems, these devices are indispensable in modern infrastructure. Furthermore, sectors like food processing and pharmaceuticals heavily rely on effective cooling solutions provided by refrigeration condenser coils to ensure product quality and compliance with safety standards.
Working Principles of Water-Cooled Condensers
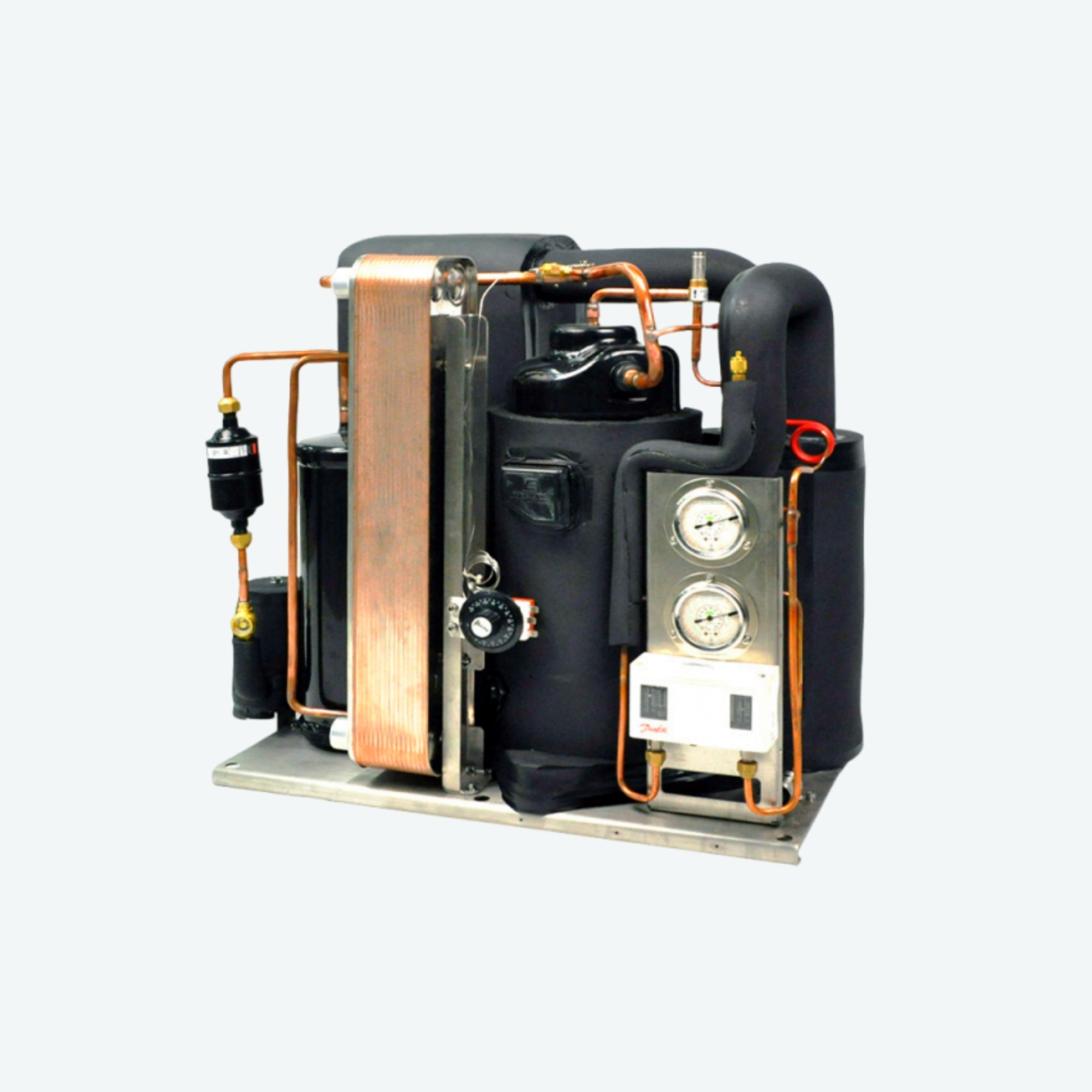

Water-cooled condensers play a pivotal role in the refrigeration process, ensuring that heat is effectively dissipated from the system. These units utilize water as a cooling medium to enhance efficiency compared to air-cooled systems. By understanding how heat exchange occurs within these systems, we can appreciate their importance in various applications, particularly in industrial settings where large amounts of heat must be managed.
How Heat Exchange Occurs
Heat exchange in a water-cooled condenser involves the transfer of thermal energy from the refrigerant to the cooling water circulating through the system. As hot refrigerant gas enters the condenser, it flows through a series of coils or tubes where it encounters cooler water. This interaction allows heat to dissipate efficiently, converting the refrigerant gas into liquid form while simultaneously warming up the water that exits and is often reused or discharged.
The design of the condenser and coil significantly influences its performance; larger surface areas and optimized flow paths facilitate better heat transfer rates. The effectiveness of this process means that water-cooled refrigeration systems can maintain lower operational temperatures, leading to enhanced overall efficiency. In essence, these units thrive on their ability to manage temperature gradients effectively.
Role of Refrigerant and Water
In any refrigeration condenser setup, both refrigerant and water are crucial players in achieving optimal performance. The refrigerant carries absorbed heat from inside a space or process; as it passes through the condenser coil, it releases this heat into the circulating water. Meanwhile, this cooling medium absorbs energy from the refrigerant and subsequently transfers it away from the system.
The interaction between these two fluids—refrigerant and water—is what makes a liquid cooled chiller particularly effective in maintaining desired temperatures within industrial applications. This synergy not only enhances cooling capabilities but also ensures that systems remain efficient over time by minimizing energy consumption during operation. Consequently, understanding how each component interacts aids operators in optimizing their setups for maximum performance.
Efficiency Factors in Operation
Several factors influence how efficiently a water-cooled refrigeration system operates, including ambient conditions, flow rates of both refrigerant and cooling water, and maintenance practices. For instance, higher ambient temperatures can challenge even well-designed systems; thus proper sizing is essential for peak performance under varying conditions. Additionally, consistent monitoring of fluid flow rates helps ensure that both refrigerants within their respective coils are adequately cooled.
Regular maintenance is vital for ensuring longevity and efficiency within these systems as well; neglected components can lead to reduced performance over time due to fouling or scaling on condenser surfaces which hinders effective heat transfer processes. Therefore investing time into routine checks will pay dividends by extending equipment lifespan while maintaining optimal operating conditions for your chiller water unit or any related machinery using a refrigeration condenser coil setup.
Types of Water-Cooled Condensers
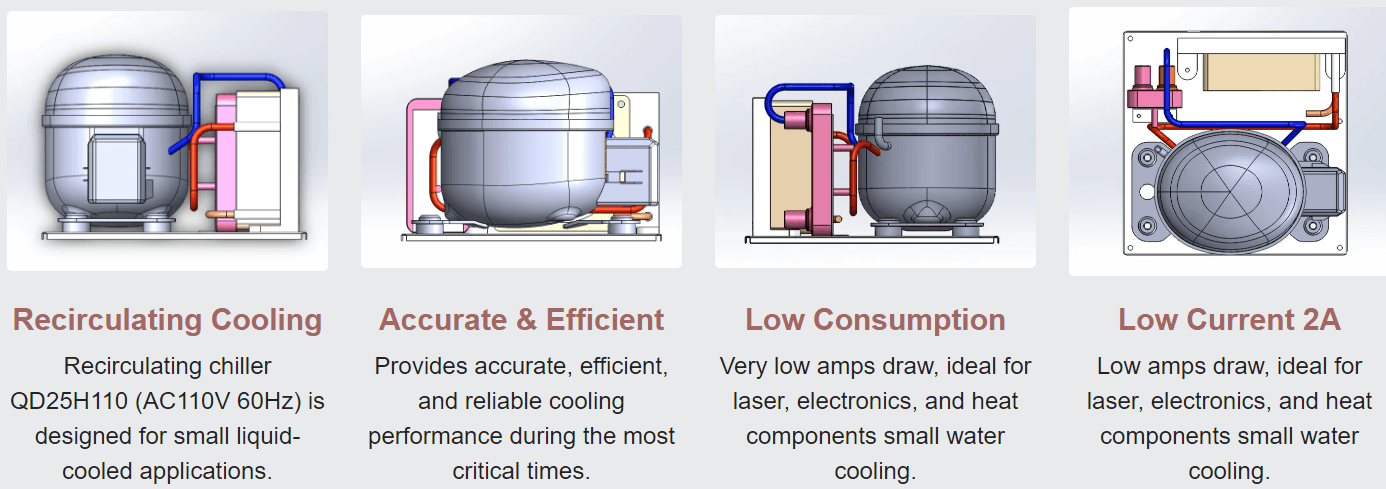
When it comes to water-cooled condensers, variety is the spice of life! Each type serves specific needs and applications, ensuring optimal performance for various refrigeration systems. Understanding these types helps in selecting the right refrigeration condenser for your needs.
Shell and Tube Condensers
Shell and tube condensers are a popular choice in many industrial applications due to their robust design and efficiency. These units consist of a series of tubes enclosed within a cylindrical shell, allowing the refrigerant to flow through the tubes while water circulates around them. Their ability to handle large volumes of refrigerant makes them ideal for high-capacity water-cooled chillers, ensuring effective heat exchange.
In terms of maintenance, shell and tube condensers are relatively easy to clean and service, which is crucial for sustaining long-term performance. The condenser coil's design also allows for flexibility in configuration, accommodating various operational requirements. This versatility makes shell and tube condensers a staple in water-cooled refrigeration systems across industries.
Plate Condensers
Plate condensers offer another efficient option for those looking into water-cooled solutions. Comprising thin plates stacked together, these units maximize surface area while minimizing space requirements—a perfect match for compact installations! The design promotes excellent heat transfer efficiency as refrigerant flows between plates while cooling water circulates on the opposite side.
One significant advantage of plate condensers is their ease of installation; they can be integrated seamlessly into existing systems without extensive modifications. Additionally, their lightweight nature reduces structural load concerns often associated with larger condenser types. With a growing demand for energy-efficient solutions, plate condensers are increasingly favored in both commercial and residential applications.
Evaporative Condensers
Evaporative condensers combine the principles of both cooling towers and traditional water-cooled systems, making them highly efficient options for large-scale refrigeration needs. These units utilize both air and water to cool refrigerants effectively; as warm refrigerant vapor enters the condenser coil, it passes through wet surfaces where evaporation occurs—cooling it down rapidly! This dual-action not only enhances efficiency but also reduces overall water usage compared to standalone cooling methods.
The evaporative condenser’s design allows it to operate effectively even in high ambient temperatures by leveraging evaporative cooling principles. They are particularly advantageous in industries where space is limited but cooling demands remain high—think food processing or chemical manufacturing! However, regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance since mineral buildup can hinder efficiency over time.
Integrating Water-Cooled Chillers
Water-cooled chillers play a pivotal role in modern refrigeration systems, offering enhanced efficiency and reliability. By integrating water-cooled chillers into your setup, you can leverage their unique features to optimize cooling performance. This section delves into the characteristics of mini water chillers, the benefits for OEM and ODM projects, and the essential components found in Arctic active cooling systems.
Features of Mini Water Chillers
Mini water chillers are compact yet powerful units designed to provide effective cooling without taking up excessive space. These water-cooled chillers utilize a refrigeration condenser coil that efficiently transfers heat away from the refrigerant, ensuring optimal performance even in tight environments. With their advanced design, mini water chillers often come equipped with features like variable speed compressors and integrated controls that enhance energy efficiency while maintaining consistent temperature levels.
The versatility of these units makes them suitable for various applications—from small commercial setups to residential uses—where space is at a premium but cooling needs remain high. Additionally, many mini water chillers are designed for easy installation and maintenance, making them an attractive option for users who prioritize convenience alongside performance. Given their efficient operation, these liquid cooled chillers not only save on energy costs but also contribute to a more sustainable approach to refrigeration.
Benefits for OEM and ODM Projects
In the realm of Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) and Original Design Manufacturer (ODM) projects, integrating water-cooled refrigeration solutions offers numerous advantages that can set your product apart from competitors. First off, utilizing a reliable water cooled condenser enhances system efficiency by ensuring optimal heat exchange through its advanced design features—resulting in lower operational costs over time. Furthermore, employing these systems allows for greater customization options tailored to specific project requirements.
Another significant benefit lies in the scalability of water cooled chiller systems; they can be adapted easily as project demands evolve or expand without sacrificing performance or efficiency. This adaptability is particularly crucial in industries where rapid changes are common—such as food service or pharmaceuticals—ensuring your products remain viable over time. Ultimately, investing in high-quality refrigeration condenser coils within your designs can lead to improved customer satisfaction due to enhanced reliability and lower energy consumption.
Key Components in Arctic Active Cooling Systems
Arctic active cooling systems rely on several key components that work together seamlessly to achieve superior thermal management through efficient heat exchange methods involving a well-designed condenser and coil setup. The primary elements include the compressor—responsible for circulating refrigerant—and the evaporator coil that absorbs heat from the environment before transferring it through the refrigeration condenser coil back into chilled liquid form.
Moreover, effective integration also requires robust pumps and control mechanisms that regulate flow rates within these chiller water units while maintaining optimal operating conditions under varying loads. The synergy among these components ensures peak performance across diverse applications ranging from industrial processes to commercial HVAC systems needing precise temperature control during peak demand periods. As technology advances further into eco-friendly practices, expect innovations around these key components driving even greater efficiencies within future Arctic active cooling solutions.
Advantages of Water-Cooled Refrigeration
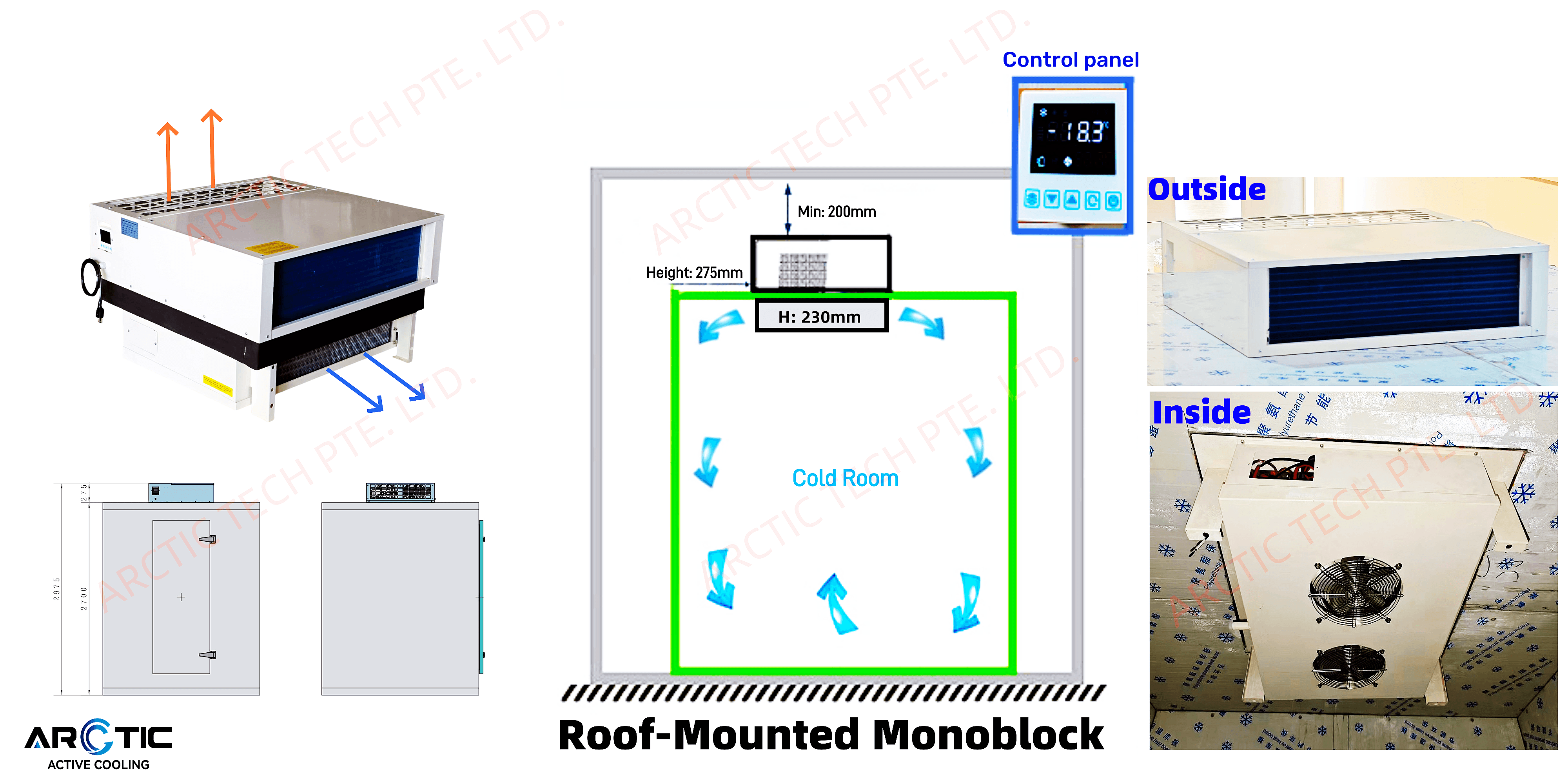
Water-cooled refrigeration systems offer a variety of advantages over their air-cooled counterparts, making them an attractive option for numerous applications. These systems utilize water as the primary medium for heat exchange, which significantly enhances their efficiency and effectiveness in cooling environments. By understanding the benefits of water-cooled condensers, businesses can make informed decisions about their refrigeration needs.
Enhanced Efficiency Over Air-Cooled Systems
One of the standout features of water-cooled condensers is their superior efficiency compared to air-cooled systems. The ability to maintain lower temperatures in the condenser and coil allows for better heat transfer, leading to reduced energy consumption during operation. Additionally, water has a higher thermal conductivity than air, enabling refrigeration condensers to dissipate heat more effectively and ensuring optimal performance even under high demand.
Space-Saving Design Benefits
In today's world where real estate is at a premium, space-saving design benefits are crucial for many industries. Water-cooled refrigeration units typically require less physical space than air-cooled alternatives due to their compact design and efficient layout. This makes them ideal for facilities where maximizing usable space is essential.
Furthermore, the installation of a chiller water unit allows businesses to consolidate equipment into smaller areas without compromising performance or capacity. The streamlined nature of these systems also facilitates easier integration into existing infrastructures or new builds alike. Ultimately, this space efficiency not only helps with operational flexibility but also contributes positively to aesthetic considerations in facility design.
Cost-Effectiveness in Long-Term Use
While the initial investment in a water cooled condenser may be higher than that of an air-cooled system, the long-term cost-effectiveness cannot be overlooked. Reduced energy consumption translates directly into lower operating costs over time; thus allowing companies to recoup their investment quicker than expected through savings on electricity bills alone.
Moreover, maintenance requirements tend to be less frequent with water cooled refrigeration systems due to fewer moving parts exposed to outdoor elements like dust and debris found in air-cooling units. This reliability leads not only to decreased maintenance costs but also extends equipment lifespan significantly when compared with traditional options like refrigeration condenser coils used in air-based systems.
Ultimately, choosing a liquid cooled chiller or any other form of water-cooled technology presents compelling advantages worth considering by any business looking towards future-proofing its operations while enjoying enhanced performance today.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our exploration of water-cooled condensers, it’s clear that these systems play a pivotal role in modern refrigeration. Their efficiency and effectiveness in heat exchange make them indispensable across various industries, from food preservation to large-scale HVAC solutions. As we look to the future, advancements in technology promise even greater efficiencies and capabilities for water-cooled refrigeration systems.
The Future of Water-Cooled Technology
The future of water-cooled technology is bright, with innovations driving improvements in performance and sustainability. As energy efficiency becomes a priority, manufacturers are focusing on developing more advanced condenser and coil designs that optimize heat transfer while minimizing water usage. Additionally, the integration of smart technologies will allow for better monitoring and management of liquid cooled chillers, ensuring they operate at peak efficiency.
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
To keep your water-cooled condenser operating smoothly, regular maintenance is essential. Start by routinely checking the refrigeration condenser coil for any signs of corrosion or buildup that could hinder performance; cleaning these components can significantly enhance efficiency. Furthermore, ensure that the chiller water unit is properly maintained by monitoring flow rates and temperatures—this proactive approach can prevent costly breakdowns and extend the lifespan of your equipment.
Choosing the Right Water-Cooled Solution
When selecting a water-cooled solution for your needs, consider factors such as system size, application requirements, and energy efficiency ratings. Look for reputable brands offering reliable products like water cooled chillers that meet industry standards while providing excellent performance characteristics. By carefully evaluating your options and understanding how each component interacts within the broader context of water cooled refrigeration systems, you can make an informed decision that maximizes both cost-effectiveness and operational reliability.
