Introduction

"Arctic Active Cooling. Endless Possibilities. We capture new technologies in mobile and compact cooling. Full-size cooling in a miniature design, customized to make your device stand out with innovative thermal management."
In the world of refrigeration and air conditioning, understanding the intricacies of a compressor condensing unit (CCU) is essential for effective cooling solutions. A CCU plays a pivotal role in managing temperature and ensuring that various applications, from commercial refrigeration to residential air conditioning, operate efficiently. As we delve into this topic, we will clarify what a condensing unit is, explore its key components, and highlight its diverse applications.
What is a Compressor Condensing Unit?
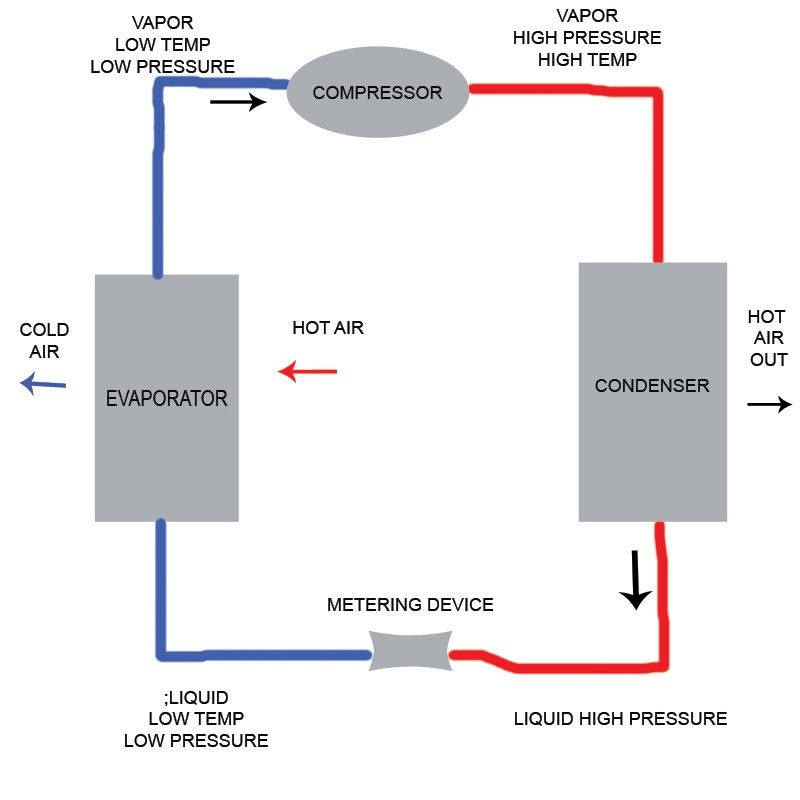
At its core, a compressor condensing unit is an integral part of many refrigeration systems. It combines the functions of both compression and condensation within one compact assembly, making it crucial for heat exchange processes. Essentially, the CCU facilitates the transfer of heat from inside an environment to the outside, effectively maintaining desired temperatures.
Key Components of a CCU
A typical compressor condensing unit consists of several key components that work harmoniously together. These include the compressor itself, which compresses refrigerant gas; the condenser coil where heat dissipation occurs; and fans that assist in air movement across these coils. Understanding these components helps clarify how they contribute to efficient cooling systems and answers questions like What is the difference between a compressor and a condensing unit?
Applications of Condensing Units
Condensing units find their place in various applications across different industries due to their versatility and efficiency. From supermarket refrigeration systems to HVAC setups in commercial buildings, CCUs are everywhere! They are also popular in smaller setups such as residential air conditioners or even specialized equipment like those using Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Units—showcasing their adaptability in modern cooling technologies.
Understanding the Basics of Compressor Condensing Units

When diving into the world of refrigeration, it’s essential to grasp the concept of a compressor condensing unit (CCU). This unit is a vital component in various cooling systems, playing a crucial role in maintaining desired temperatures. Understanding what a condensing unit is and how it operates can significantly enhance our appreciation for modern refrigeration technology.
Definition of a Condensing Unit
A condensing unit is essentially the heart of many refrigeration systems, responsible for transforming refrigerant from gas to liquid form. This process occurs through heat exchange, where the refrigerant releases absorbed heat into the environment. In simpler terms, when we ask ourselves, What is a condensing unit? we are looking at a sophisticated system that ensures efficient cooling by facilitating this critical phase change.
In practical applications, CCUs are commonly found in air conditioning systems and commercial refrigeration setups. They consist of several components working together, including compressors, condensers, and fans. By understanding this definition and its components, one can better appreciate how these units contribute to effective temperature control.
Functions of the Compressor in a CCU
The compressor serves as the engine behind any compressor condensing unit (CCU), performing several key functions that are indispensable for efficient operation. Primarily, it compresses low-pressure refrigerant gas into high-pressure gas before sending it to the condenser coil for heat release. This compression process not only raises the temperature but also prepares the refrigerant for its next phase in the cooling cycle.
Moreover, without an effective compressor functioning within a CCU or any refrigeration system at all, achieving optimal cooling would be nearly impossible. It acts as both pump and pressure regulator while ensuring that refrigerants circulate smoothly throughout the system. Thus, understanding what is compressor condenser becomes pivotal when exploring how these units maintain desired temperatures.
Role of Refrigerants in Condensing Units
Refrigerants are integral to any discussion about compressor condensing units; they act as carriers of heat within these systems. The choice of refrigerant directly affects efficiency and performance—common options include R134a and R290 due to their favorable thermal properties and lower environmental impact compared to older alternatives like CFCs. When considering What is condensate in an air compressor? it's essential to note that proper refrigerant management helps minimize unwanted moisture accumulation.
In essence, refrigerants enable CCUs to absorb heat from indoor spaces effectively while releasing it outdoors during condensation cycles. Their chemical properties dictate how well they perform under varying temperatures and pressures—crucial factors for maintaining efficiency in both residential and commercial applications alike. As we delve deeper into refrigeration technology trends later on, understanding these roles will prove increasingly valuable.
What is the Difference Between a Compressor and a Condensing Unit?

When diving into refrigeration systems, understanding the distinction between a compressor and a condensing unit is crucial. A compressor condensing unit (CCU) integrates multiple components to facilitate efficient cooling processes, while the compressor itself serves as one of those key components. So, what is the difference between a compressor and a condensing unit? Let’s break it down.
Distinct Roles in Refrigeration
In refrigeration systems, each component has its unique role that contributes to overall function. The compressor's primary job is to compress refrigerant gas, increasing its pressure and temperature before sending it to the condenser. Conversely, what is a condensing unit? It encompasses not only the compressor but also other elements like condensers and evaporators that work together to convert refrigerant from gas back into liquid form, enabling effective heat exchange.
Understanding these distinct roles helps clarify why both components are necessary for optimal performance in cooling applications. While compressors handle gas compression, CCUs manage the entire refrigeration cycle from start to finish. This synergy ensures that temperatures remain low where needed—whether in commercial refrigeration or air conditioning systems.
Mechanical vs. Thermal Components
The difference between mechanical and thermal components further illustrates how compressors and condensing units operate within refrigeration systems. Compressors are primarily mechanical devices; they rely on moving parts to compress refrigerants efficiently while maintaining durability over time. On the other hand, condensing units include thermal components such as coils that facilitate heat transfer during condensation.
These mechanical parts within a CCU work alongside thermal elements to create an efficient cooling process. While compressors may be considered more of an engine driving the system's functionality, condensing units represent an entire ecosystem designed for effective temperature regulation through various phases of refrigerant flow—liquid and gas alike.
How They Work Together
The collaboration between compressors and condensing units exemplifies how complex systems achieve efficiency in cooling applications. In essence, when you ask What is condensate in an air compressor? you're looking at one aspect of this teamwork: as refrigerant transitions through its phases during this collaborative effort, it generates condensate which must be managed effectively for optimal performance.
The mini DC compressor found in models like Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Unit showcases this teamwork beautifully—by directly contacting evaporators without needing secondary coolants or extensive ductwork. This direct expansion system minimizes complexity while maximizing efficiency by allowing refrigerants like R134a or R290 to absorb heat right at their source without additional mechanical burdens.
In conclusion, understanding how compressors fit into larger CCUs can illuminate their importance in refrigeration technology today—highlighting not just distinct functions but also interdependence essential for performance excellence across various applications including those found within Condensing Units for Refrigeration Systems.
The Ins and Outs of the Mini DC Compressor

Features of the Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Unit
The Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Unit is designed for direct contact with the user’s evaporator or cold plate, eliminating the need for secondary coolants. This unique setup significantly reduces complexity by minimizing parts such as fans and pumps, which are often required in traditional systems. By doing away with ductwork and extensive piping, this compressor condensing unit streamlines installation and enhances overall efficiency.
Moreover, its ultra-compact design means it can fit into tight spaces without sacrificing performance. The integration of a mini DC compressor allows for direct heat absorption at the source, making it exceptionally effective in maintaining desired temperatures. In essence, this CCU (compressor-condenser unit) redefines convenience while ensuring high heat transfer rates through its innovative direct expansion system.
Direct Expansion System Explained
The direct expansion system is central to understanding how the Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Unit operates effectively. Unlike traditional systems that rely on indirect cooling methods involving secondary coolants, this approach drives refrigerant directly through the evaporator using a mini compressor. This not only simplifies the process but also maximizes heat transfer efficiency by allowing refrigerant to absorb heat right at its source.
What is a condensing unit if not an essential component that facilitates this direct interaction? By minimizing intermediary steps in heat exchange, users benefit from quicker cooling times and reduced energy consumption—two aspects that are increasingly vital in today's eco-conscious market. It's clear that knowing what is the difference between a compressor and a condensing unit becomes essential when evaluating their respective roles within such systems.
Benefits of Using R134a and R290 Refrigerants
When discussing refrigerants used in these advanced systems, R134a and R290 stand out due to their environmental compatibility and performance characteristics. Both options are known for their low global warming potential compared to older refrigerants like R22 or R12, making them more suitable for modern applications where sustainability matters more than ever.
Additionally, these refrigerants work exceptionally well with mini compressors found in CCUs like the Arctic Active Cooling model because they facilitate efficient heat transfer without compromising system integrity or safety standards. So whether you're pondering what condensate in an air compressor might mean for your setup or simply looking to upgrade your refrigeration technology, considering these refrigerant options can lead to significant operational benefits.
What is Condensate in an Air Compressor?

When discussing compressor condensing units, one often encounters the term condensate. But what is condensate in an air compressor? Simply put, it refers to the moisture that forms when humid air cools down inside the compressor system. This moisture can accumulate and lead to various performance issues if not properly managed.
Understanding Condensate Formation
Condensate formation occurs primarily due to temperature differences within the compressor condensing unit (CCU). As warm, moist air enters the system and comes into contact with cooler surfaces, such as coils or pipes, water vapor condenses into liquid droplets. This process is a natural part of refrigeration systems; however, excessive condensate can create problems that affect overall efficiency.
In a CCU, understanding how and when condensate forms is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. If left unchecked, this buildup can lead to corrosion or even mechanical failures over time. Therefore, recognizing what contributes to condensate formation helps users implement effective management strategies.
Effects of Condensate on Performance
The presence of condensate in an air compressor can significantly impact its performance and longevity. First off, excessive moisture can dilute lubricants and create sludge that clogs critical components of the compressor condensing unit. This not only reduces efficiency but may also lead to costly repairs.
Moreover, condensate accumulation can disrupt airflow within the system, causing temperature imbalances that hinder cooling effectiveness. Users may notice fluctuating temperatures or increased energy consumption as their CCU struggles to maintain proper operation under these adverse conditions. Hence, understanding the effects of condensate helps users appreciate why effective management solutions are necessary.
Solutions to Manage Condensate
Managing condensate effectively in a compressor condensing unit involves several strategies tailored for optimal performance. One common solution is installing a drain trap or separator designed specifically for removing excess water from the system without interrupting airflow or cooling processes. These devices ensure that any collected moisture does not interfere with other components.
Another approach includes regular maintenance routines where users check for leaks or signs of corrosion caused by accumulated condensation. Implementing routine inspections allows early detection of potential issues before they escalate into major problems affecting system efficiency and reliability.
Finally, considering advanced technologies such as those found in Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Units could further enhance moisture management capabilities while reducing complexity within your setup—no secondary coolant needed! Such innovations streamline operations while addressing concerns related to what is condensate in an air compressor effectively.
Condensing Units for Refrigeration Systems
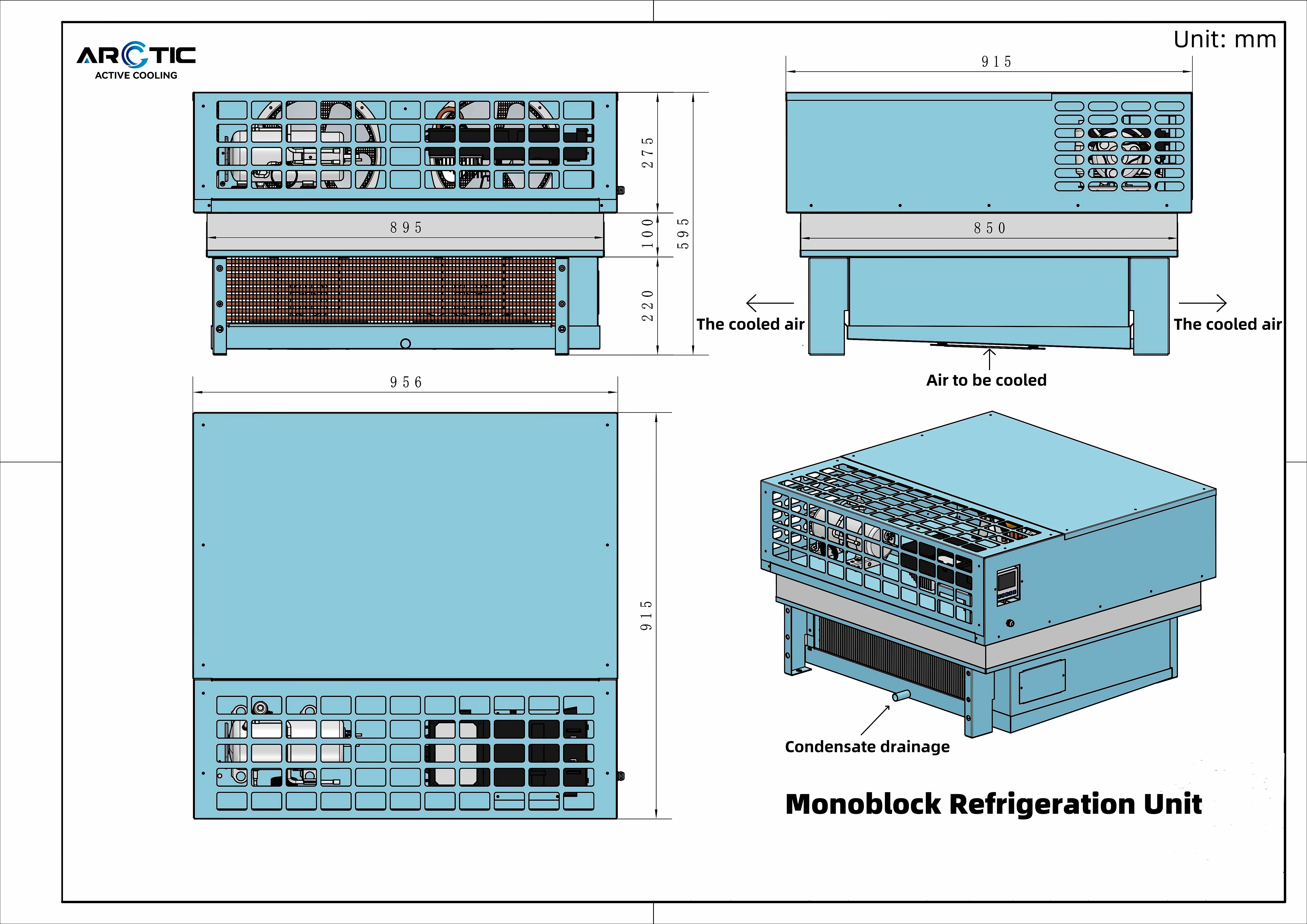
When it comes to refrigeration systems, the compressor condensing unit (CCU) plays a pivotal role in ensuring efficient cooling and temperature control. These units are integral to various applications, from commercial refrigeration to air conditioning systems. Understanding how these condensing units function and their impact on overall system efficiency is essential for anyone involved in refrigeration technology.
Types of Refrigeration Systems Utilizing CCUs
Compressor condensing units are utilized in a variety of refrigeration systems, including walk-in coolers, display cases, and industrial chillers. Each application leverages the unique capabilities of a CCU to maintain optimal temperatures effectively. Additionally, mini DC compressors are gaining traction due to their compact size and direct integration with evaporators or cold plates, reducing complexity and improving efficiency.
In contrast to traditional systems that rely on extensive ductwork and piping, the Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Unit simplifies installation by minimizing additional components. This direct expansion system allows for higher heat transfer rates while using R134a or R290 refrigerants efficiently. As industries seek more streamlined solutions for cooling needs, understanding what is a condensing unit becomes increasingly important.
Efficiency and Cost Benefits
The use of compressor condensing units brings significant efficiency gains and cost benefits across various refrigeration applications. By eliminating unnecessary parts such as fans or pumps that circulate coolant or air, CCUs reduce energy consumption significantly. This translates into lower operational costs over time while providing reliable cooling performance.
Moreover, the compact design of modern CCUs like the Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Unit allows businesses to save on space without sacrificing performance. The direct expansion system minimizes refrigerant loss during operation as it drives heat absorption directly at the source. Consequently, businesses can enjoy enhanced productivity while keeping costs in check—an attractive proposition for any budget-conscious operator.
Future Trends in Refrigeration Technology
As we look toward the future of refrigeration technology, several trends are reshaping how compressor condensing units operate within various systems. Innovations such as smart controls and IoT integration will enable real-time monitoring and optimization of cooling processes—leading us closer to energy-efficient solutions that reduce environmental impact significantly.
Additionally, advancements in refrigerants will continue to play a crucial role; alternatives like R290 offer lower global warming potential compared to traditional options while maintaining effective cooling capabilities within CCUs. As industries become more aware of sustainability issues related to what is condensate in an air compressor or other components affecting performance, embracing these changes will be vital for staying competitive.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the compressor condensing unit (CCU) is crucial for anyone involved in refrigeration systems. A CCU plays an integral role in cooling applications, utilizing key components like compressors and condensers to efficiently manage heat transfer. By grasping what a condensing unit is and how it operates, users can make informed decisions about their refrigeration needs.
Key Takeaways on Compressor Condensing Units
To clarify, a compressor condensing unit combines both the compressor and condenser functions to effectively manage refrigerants within a system. It's essential to understand what is the difference between a compressor and a condensing unit; while the former compresses refrigerant gas, the latter cools it down into liquid form. Furthermore, the diverse applications of CCUs—from commercial refrigeration to HVAC systems—highlight their versatility and importance in modern technology.
Importance of Proper Maintenance
Proper maintenance of your compressor condensing unit cannot be overstated; it ensures optimal performance and longevity of the system. Neglecting maintenance can lead to issues such as increased energy consumption or even complete system failure due to factors like condensate in an air compressor affecting performance. Regular checks not only help identify potential problems early but also keep your CCU running smoothly and efficiently.
Exploring Advanced Technologies in Condensing Units
As technology advances, exploring new innovations in compressor condenser units becomes increasingly important for enhancing efficiency and effectiveness in refrigeration systems. The Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Unit exemplifies cutting-edge design by eliminating unnecessary ductwork and minimizing component count while maximizing heat transfer rates with its direct expansion system setup. As we look ahead, staying informed about developments such as these will prepare users for future trends that promise even greater efficiency in managing refrigerants.
