Introduction
"Arctic Active Cooling. Endless Possibilities. We capture new technologies in mobile and compact cooling. Full-size cooling in a miniature design, customized to make your device stand out with innovative thermal management."
In the world of refrigeration, condensing units play a pivotal role in ensuring systems operate efficiently and effectively. Understanding condensing units refrigeration is essential for anyone involved in the design, maintenance, or operation of cooling systems. These units are at the heart of various applications, from commercial refrigeration to residential air conditioning.
Understanding Condensing Units Refrigeration
So, what is a condensing unit in refrigeration? At its core, it’s a crucial component that helps convert refrigerant gas back into liquid form after it has absorbed heat from the environment. This process is central to the refrigeration cycle and involves several components working harmoniously to maintain desired temperatures.
Importance of Efficient Refrigeration Systems
The importance of efficient refrigeration systems cannot be overstated; they save energy, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact. As industries strive for sustainability, understanding what is the function of a condensing unit becomes vital for optimizing performance and reliability. Efficient systems not only enhance user experience but also contribute significantly to energy conservation efforts.
Overview of Direct Expansion Systems
Direct expansion systems are an innovative approach within the realm of condensing units refrigeration. These systems utilize direct contact between refrigerant and evaporator surfaces to achieve optimal heat transfer rates with minimal complexity. The Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Unit exemplifies this technology by eliminating secondary coolants and reducing ductwork needs—making it easier to integrate into existing equipment without sacrificing efficiency.
What is a Condensing Unit in Refrigeration?

Condensing units play a pivotal role in the world of refrigeration, acting as the heart of many cooling systems. They are responsible for transforming refrigerant from gas to liquid, which is essential for maintaining desired temperatures in various applications. Understanding what a condensing unit in refrigeration entails is crucial for anyone looking to optimize their cooling processes.
Definition and Components
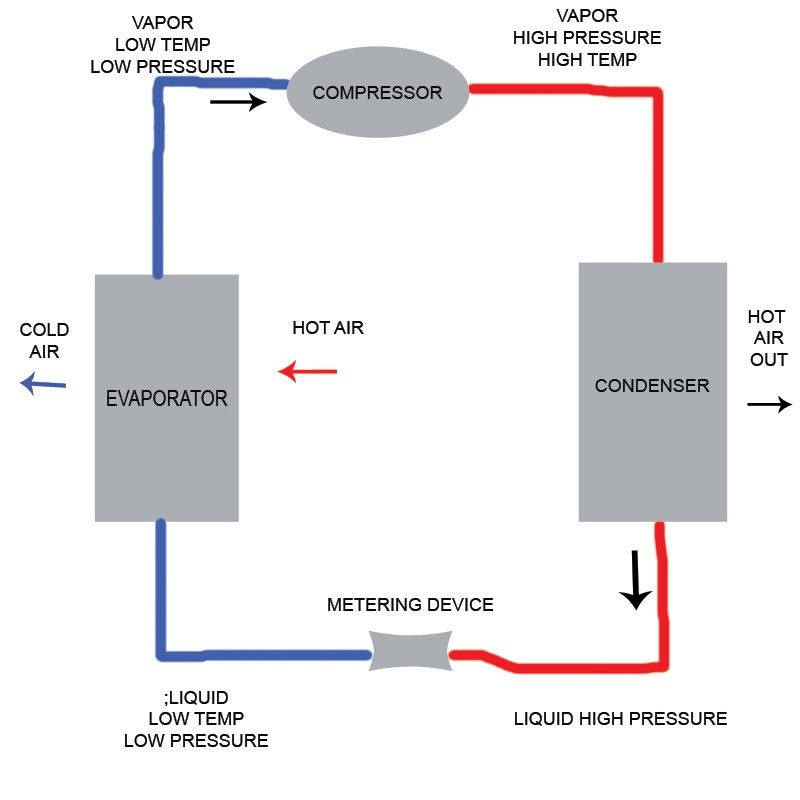
A condensing unit in refrigeration comprises several key components, including a compressor, condenser coil, expansion valve, and evaporator. The compressor compresses the refrigerant gas, raising its pressure and temperature before it moves to the condenser coil. Here, the refrigerant releases heat to the surrounding environment and changes back into a liquid state—this process is vital for what is the function of a condensing unit.
The components work together seamlessly to ensure efficient operation within refrigeration systems. In essence, these units are designed to maximize heat exchange while minimizing energy consumption—a critical aspect for businesses aiming for efficiency in their refrigeration needs. By understanding these components, users can better appreciate how condensing units refrigeration influences overall system performance.
Types of Condensing Units
There are several types of condensing units available on the market today, each tailored to specific applications and environments. Common types include air-cooled and water-cooled condensing units; air-cooled versions use ambient air to cool refrigerants while water-cooled ones rely on water sources like cooling towers or chillers. Additionally, there are also packaged systems that combine multiple functions into one compact unit.
Different types cater to varying needs; for instance, air-cooled models may be preferred in locations with limited space or where water resources are scarce. Meanwhile, water-cooled systems might be favored in industrial settings where efficiency demands higher heat exchange rates. Understanding these distinctions helps users select appropriate solutions based on their unique requirements—key when considering what is the difference between a condenser and a condensing unit.
Overview of Arctic Active Cooling
Arctic Active Cooling offers an innovative approach with its DC Condensing Unit that significantly simplifies traditional refrigeration setups. This direct expansion system operates by being directly connected to the user’s evaporator or cold plate without requiring secondary coolants or complex circulation methods like fans or pumps. This streamlined design minimizes parts involved while maximizing efficiency—a noteworthy advantage over conventional systems.
The Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Unit utilizes R134a or R290 refrigerants and features an ultra-compact design thanks to its mini DC compressor that drives refrigerant directly through the evaporator itself. This direct method allows heat absorption right at the source while reducing ductwork and piping requirements significantly—making installation easier than ever before! By eliminating unnecessary complexity from standard setups, this technology exemplifies how modern innovations can enhance what is the use of a condenser in refrigeration applications.
What is the Function of a Condensing Unit?
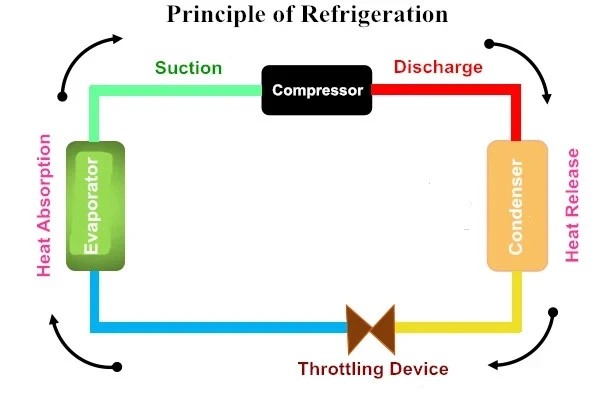
Condensing units play a crucial role in the refrigeration cycle, acting as the heartbeat of efficient cooling systems. They are essential components that help convert refrigerant from gas to liquid, facilitating effective heat exchange and temperature control. Understanding what is the function of a condensing unit is vital for anyone involved in refrigeration technology.
Role in Refrigeration Cycle
In the refrigeration cycle, condensing units are responsible for expelling heat absorbed by the refrigerant from the evaporator. This process begins when the refrigerant, having absorbed heat from its surroundings, enters the condensing unit as a low-pressure gas. Once inside, it gets compressed into a high-pressure gas before releasing its heat and transforming back into a liquid state—essentially allowing for continuous cooling.
The efficiency of condensing units refrigeration directly impacts overall system performance. A well-functioning unit ensures that heat is effectively removed from the refrigerated space, maintaining desired temperatures. In essence, without these units fulfilling their role in the refrigeration cycle, cooling would be ineffective or entirely impossible.
Heat Exchange Process
The heat exchange process within condensing units involves transferring thermal energy between two fluids—typically refrigerant and air or water—through coils or other surfaces designed for maximum efficiency. As high-pressure gas enters the condenser coils, it releases its stored heat to either ambient air or circulating water outside of the system. This phase change—from gas to liquid—is fundamental to how cooling occurs in various applications.
What is a condensing unit in refrigeration? It's not just about compression; it's also about effective heat management through this exchange process. The more efficiently this transfer occurs, the less energy is consumed overall—meaning lower operational costs and reduced environmental impact.
Importance of Temperature Control
Temperature control is paramount in any refrigeration application, whether it's food storage or industrial processes requiring precise climate conditions. Condensing units ensure that temperatures remain stable by continuously cycling refrigerant through its system while adapting to load changes based on demand. This capability helps prevent spoilage and maintains product quality across various industries.
Moreover, understanding what is the use of a condenser in refrigeration expands our grasp on how these systems function holistically within larger setups like Arctic Active Cooling systems. These direct expansion systems minimize complexity by reducing ductwork and piping while maximizing efficiency—showcasing just how critical temperature control truly is.
What is the Difference Between a Condenser and a Condensing Unit?

Understanding the distinction between a condenser and a condensing unit is crucial for anyone involved in condensing units refrigeration. While both terms are often used interchangeably, they refer to different components within the refrigeration system. Clarifying these differences helps in optimizing system performance and efficiency.
Clarifying Terminology
A condenser is specifically designed to convert refrigerant vapor into liquid by removing heat from it, while a condensing unit encompasses not only the condenser but also additional components like compressors and fans. In essence, when we ask, What is a condensing unit in refrigeration? we're referring to an entire assembly that plays a pivotal role in cooling systems. This distinction is vital for understanding how each component contributes to overall efficiency and functionality.
Functionality Differences
When exploring What is the function of a condensing unit?, it's essential to recognize that it integrates multiple functions—compression, condensation, and sometimes even expansion—into one cohesive unit. The condenser's primary role focuses solely on heat exchange, whereas the condensing unit manages the entire refrigeration cycle. This multi-functionality allows for improved energy efficiency and reduced complexity in systems like Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Units.
Practical Implications for Users
For users considering their options in refrigeration technology, knowing What is the use of a condenser in refrigeration? can influence purchasing decisions significantly. A standalone condenser might be suitable for specific applications where space allows; however, opting for an integrated condensing unit can streamline installation and maintenance processes. By understanding these distinctions, users can make informed choices that enhance both performance and cost-effectiveness.
What is the Use of a Condenser in Refrigeration?
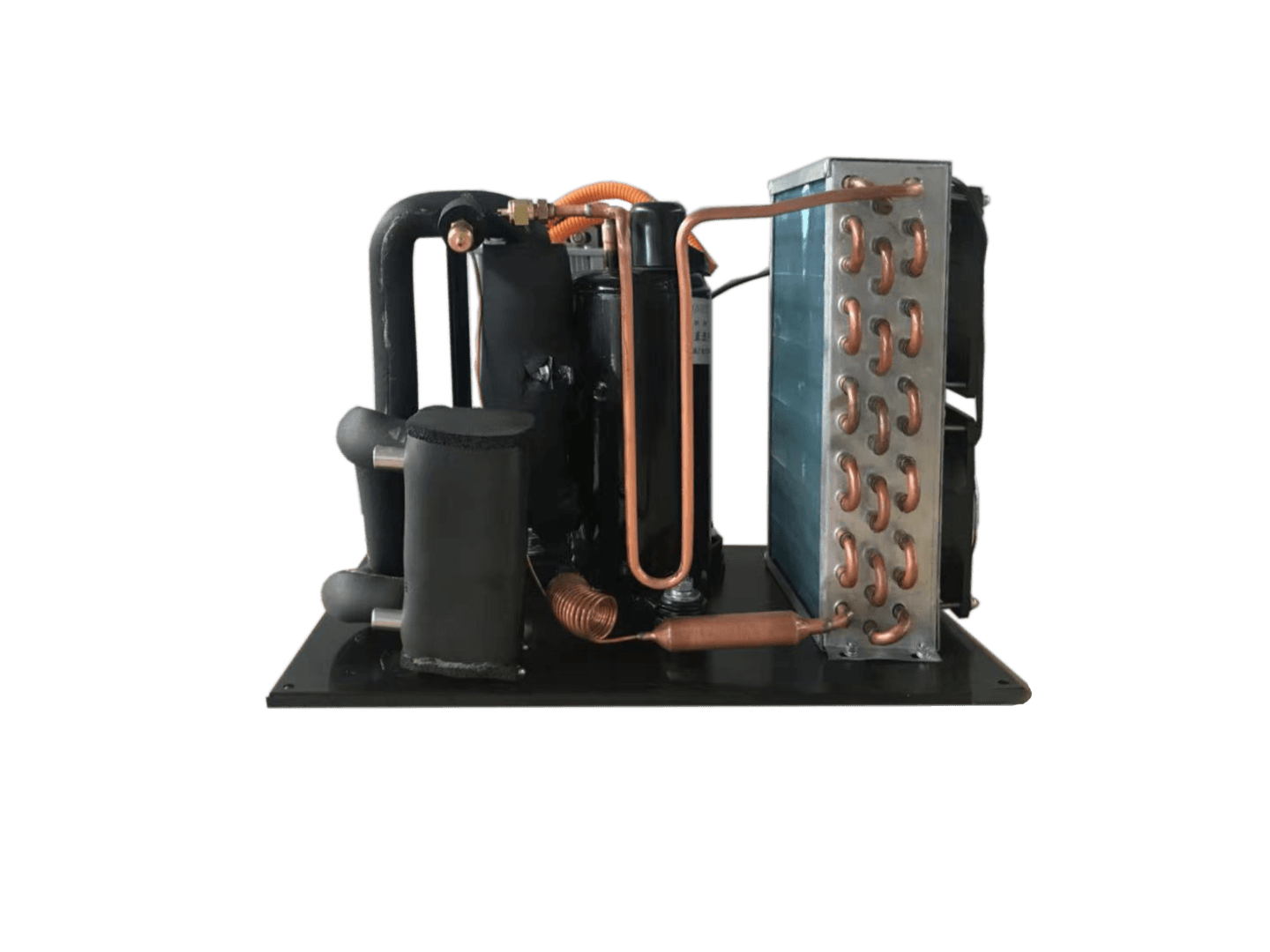

In the world of condensing units refrigeration, the condenser plays a pivotal role in ensuring efficient cooling and temperature control. Understanding what is a condensing unit in refrigeration requires recognizing that the condenser is integral to this system, facilitating heat exchange and maintaining optimal conditions for various applications. From commercial refrigeration to industrial processes, condensers are essential components that enhance overall system performance.
Specific Applications
Condensers are utilized across numerous specific applications within the refrigeration industry. For instance, they are commonly found in supermarket refrigeration systems, where they help maintain low temperatures for perishable goods by effectively removing heat from refrigerants. Additionally, condensers play a critical role in HVAC systems, ensuring that buildings remain comfortable by regulating indoor temperatures efficiently.
The versatility of condensers extends beyond just these applications; they also find use in food processing plants and cold storage facilities where precise temperature management is crucial. In these settings, understanding what is the function of a condensing unit becomes vital as it directly impacts product quality and safety. Thus, whether it's preserving food or maintaining climate control in commercial spaces, condensers are indispensable.
Efficiency Enhancements
One of the primary benefits of using a condenser in refrigeration systems lies in its ability to enhance efficiency significantly. By facilitating effective heat exchange processes, condensers help reduce energy consumption and lower operational costs over time. The integration of advanced technologies within modern condensing units refrigeration has led to improved thermal performance and reduced environmental impact.
Moreover, when considering what is the difference between a condenser and a condensing unit?, it's clear that while both serve distinct roles within the system, their combined functionality leads to greater overall efficiency. For example, utilizing an Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Unit eliminates unnecessary complexity by minimizing parts like ductwork and piping—contributing further to energy savings. Thus, incorporating efficient condensers into refrigeration systems not only optimizes performance but also promotes sustainability.
Integration with Other Systems
The seamless integration of condensers with other systems enhances their utility across various applications within condensing units refrigeration setups. When evaluating what is the use of a condenser in refrigeration contexts like food storage or HVAC systems, it becomes evident that their compatibility with other components—such as evaporators—creates more cohesive operational frameworks. This integration allows for better temperature control and more reliable cooling cycles.
Furthermore, advanced designs like those seen with Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Units illustrate how modern technology simplifies this integration process by reducing reliance on secondary coolants or complex plumbing setups—making installation easier and more cost-effective for users. As such systems continue evolving alongside advancements in refrigerant technology (like R134a or R290), understanding how these elements work together becomes increasingly important for maximizing efficiency and effectiveness.
Advantages of DC Condensing Units

In the realm of condensing units refrigeration, the DC condensing units stand out for their innovative design and efficiency. These units simplify the refrigeration process by minimizing components, which not only reduces potential points of failure but also lowers maintenance costs. Understanding what is a condensing unit in refrigeration becomes clearer when considering how these units streamline operations.
Minimal Parts and Complexity
One of the primary benefits of DC condensing units is their minimal parts and complexity. Unlike traditional systems that rely on multiple components, these direct expansion systems are designed with fewer elements, making them easier to install and maintain. This simplicity translates to lower operational costs and a more reliable system overall, addressing the question: what is the function of a condensing unit?
With fewer moving parts, there’s less chance for mechanical failure or inefficiencies that can arise from complex systems. This aspect is especially crucial in environments where reliability is paramount. In essence, by reducing complexity, users gain peace of mind knowing that their condensing units refrigeration setup won’t let them down.
Enhanced Heat Transfer Rates
When discussing what is the use of a condenser in refrigeration, one must highlight its role in heat transfer efficiency. The Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Unit excels here; it boasts enhanced heat transfer rates due to its direct contact with evaporators or cold plates. By utilizing R134a or R290 refrigerants and employing a mini DC compressor, these systems absorb heat directly at the source without unnecessary delays.
This direct interaction minimizes energy losses that typically occur through ductwork or additional coolant circulation methods found in traditional setups. The result? A more efficient cooling process that not only saves energy but also enhances overall performance—an essential factor for any user looking to optimize their refrigeration system's effectiveness.
Ductwork and Piping Reduction
Perhaps one of the most striking advantages of DC condensing units lies in their ability to reduce ductwork and piping requirements significantly. With no need for secondary coolants or extensive air circulation mechanisms, these systems offer an elegant solution to common space constraints found in many installations today. Answering what is the difference between a condenser and a condensing unit becomes apparent as you realize how much simpler this integration can be.
By eliminating bulky ducts and pipes, users can reclaim valuable space while also reducing installation costs associated with extensive plumbing work. This streamlined approach not only enhances aesthetics but also facilitates easier maintenance access—a win-win for any facility manager or technician involved with condensing units refrigeration systems.
Conclusion

In summary, condensing units refrigeration play a crucial role in maintaining efficient temperature control across various applications. Understanding what a condensing unit is in refrigeration, along with its function, helps users appreciate the intricate workings of these systems. The distinction between a condenser and a condensing unit clarifies their specific roles, enhancing operational efficiency and user knowledge.
Key Takeaways on Condensing Units Refrigeration
Condensing units refrigeration are essential components of modern cooling systems, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency. A clear understanding of what is a condensing unit in refrigeration allows users to make informed decisions about their cooling needs. Additionally, recognizing the function of a condensing unit within the broader refrigeration cycle emphasizes its importance in heat exchange processes and temperature control.
The Future of Refrigeration Technology
The future of refrigeration technology looks promising with innovations like Arctic Active Cooling DC Condensing Units leading the charge. These systems eliminate the need for secondary coolants and complex ductwork, drastically simplifying installation while maximizing efficiency. As we continue to explore what is the use of a condenser in refrigeration, advancements will likely focus on enhancing heat transfer rates and reducing energy consumption.
Maximizing Efficiency with Direct Expansion Systems
Maximizing efficiency with direct expansion systems is vital for both environmental sustainability and cost-effectiveness. By understanding what is the difference between a condenser and a condensing unit, users can better appreciate how these technologies work together to enhance overall system performance. Embracing DC condensing units not only streamlines operations but also aligns with modern demands for energy-efficient solutions in refrigerating applications.
