Introduction

"Arctic Active Cooling. Endless Possibilities. We capture new technologies in mobile and compact cooling. Full-size cooling in a miniature design, customized to make your device stand out with innovative thermal management."
In an era where climate change is at the forefront of global concerns, understanding low GWP refrigerants has never been more critical. Low GWP meaning low global warming potential refers to substances that have a significantly reduced impact on our planet's atmosphere compared to traditional refrigerants. As we delve into the world of low GWP refrigerants, we discover not just a solution for cooling needs but also a pathway toward sustainable refrigeration practices that can help mitigate environmental harm.
Understanding Low-GWP Refrigerants
Low GWP refrigerants are designed to replace high-GWP alternatives that contribute heavily to greenhouse gas emissions. When comparing low GWP refrigerant vs GWP, it becomes clear that these eco-friendly options provide effective cooling while minimizing their carbon footprint. A comprehensive low GWP refrigerant list showcases various substances available on the market today, each with unique properties and applications tailored for different refrigeration needs.
The Importance of Sustainable Refrigeration
Sustainable refrigeration isn't merely a trend; it's an essential shift in how we approach cooling technologies in both commercial and residential settings. The adoption of low GWP refrigerants plays a crucial role in reducing overall energy consumption and lowering operational costs, making it a win-win for businesses and homeowners alike. By prioritizing eco-friendly practices through the use of low GWP refrigerant chillers, we can contribute to cleaner air and a healthier planet for future generations.
How Low-GWP Refrigerants Drive Change
The transition to low GWP refrigerants is not just about compliance with regulations; it’s about driving meaningful change across industries reliant on refrigeration technology. As companies embrace these alternatives, they become catalysts for innovation in energy efficiency and environmental responsibility. Additionally, ensuring the safety of low GWP refrigerant options further encourages their adoption by providing peace of mind alongside performance benefits.
What is Global Warming Potential?

Understanding Global Warming Potential (GWP) is crucial for grasping the impact of various refrigerants on our environment. GWP measures how much heat a greenhouse gas traps in the atmosphere over a specific time period, typically 100 years, compared to carbon dioxide (CO2). A higher GWP indicates a greater potential for warming, which is why low GWP refrigerants are increasingly sought after in sustainable refrigeration practices.
Defining GWP and Its Impact
GWP serves as a benchmark for evaluating the environmental effects of different gases, including refrigerants. For instance, while CO2 has a GWP of 1, some traditional refrigerants can have GWPs in the thousands. This stark contrast highlights the importance of transitioning to low GWP alternatives that minimize environmental damage and contribute to climate change mitigation.
Comparing GWP of Common Refrigerants
When looking at common refrigerants, it's evident that many have high GWPs that significantly contribute to global warming. For example, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) like R134a can have GWPs ranging from 1,430 to over 3,000. In contrast, low GWP refrigerants like R290 (propane) boast a GWP of just 3—making them an appealing choice for anyone seeking eco-friendly options in refrigeration systems.
Recognizing the Need for Low-GWP Alternatives
The growing awareness around climate change has led to an urgent need for low GWP alternatives across various industries. As regulations tighten and consumers demand more sustainable options, businesses must consider low GWP refrigerant lists when selecting their cooling solutions. By embracing these alternatives—such as R32 or R454B—not only do we reduce our carbon footprint but also pave the way for safer and more efficient refrigeration technologies.
Benefits of Low-GWP Refrigerants

The transition to low-GWP refrigerants offers a multitude of benefits that extend beyond mere compliance with regulations. These eco-friendly alternatives not only help mitigate climate change but also enhance operational efficiency across various applications, from chillers to air conditioning systems. By understanding the advantages of low-GWP refrigerants, businesses and consumers can make informed choices that support a sustainable future.
Environmental Advantages
One of the most significant benefits of low-GWP refrigerants is their reduced impact on global warming compared to traditional options. The concept of low GWP meaning directly correlates with their ability to minimize greenhouse gas emissions, making them a critical component in combating climate change. For instance, while conventional refrigerants may have high GWP values, low-GWP alternatives significantly lower these numbers, allowing industries to contribute positively to environmental preservation.
Moreover, using low GWP refrigerants helps in protecting the ozone layer and reducing overall atmospheric pollution. This is particularly important as we face increasing scrutiny over our environmental practices. By adopting low-GWP refrigerant options, businesses can showcase their commitment to sustainability and attract environmentally-conscious consumers.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
In addition to environmental benefits, low-GWP refrigerants often lead to improved energy efficiency in refrigeration systems. Lower energy consumption translates into cost savings for businesses operating chillers and other refrigeration units—making it a win-win situation for both the wallet and the planet. As more companies recognize the advantages of integrating low GWP refrigerant technologies into their operations, they find that these systems not only perform better but also reduce operational costs over time.
Furthermore, many modern low-GWP refrigerant chillers are designed with advanced technology that maximizes performance while minimizing energy use. This means that businesses can enjoy reliable cooling solutions without breaking the bank on energy bills or maintenance costs associated with older systems using high-GWP substances. Ultimately, investing in these innovative solutions pays off both financially and environmentally.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
As governments worldwide tighten regulations surrounding greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to low-GWP refrigerants becomes essential for compliance with these standards. Companies utilizing high GWP substances may face fines or restrictions that can jeopardize their operations; thus understanding low GWP refrigerant vs GWP is crucial for maintaining legal standing within various jurisdictions. By proactively switching to compliant alternatives early on, organizations position themselves as leaders in sustainability rather than laggards facing penalties.
Additionally, regulatory bodies often provide incentives for businesses adopting eco-friendly practices—another compelling reason to consider a shift towards lower-impact options like those found on a comprehensive low GWP refrigerant list. These incentives can include tax breaks or grants aimed at encouraging sustainable development within industries reliant on refrigeration technologies.
In conclusion, embracing low-GWP refrigerants provides multiple advantages ranging from environmental protection and cost-effectiveness to regulatory compliance—all vital elements for thriving in today's eco-conscious marketplace.
Popular Low-GWP Refrigerants on the Market

The shift towards sustainable refrigeration has led to the rise of several low-GWP refrigerants that are making waves in the industry. These alternatives not only help in reducing greenhouse gas emissions but also offer practical benefits for various applications. Let's explore some of the most popular low-GWP refrigerants currently available.
R290: The Eco-Friendly Choice
R290, also known as propane, is a standout low-GWP refrigerant that boasts an impressively low GWP of just 3. This makes it a top contender when discussing low GWP refrigerant options, especially for those looking to minimize their environmental footprint. Beyond its eco-friendliness, R290 is highly efficient and can be used in a variety of chillers and cooling systems.
Safety is often a concern with any refrigerant, but R290 has proven to be safe when handled correctly, with proper training and equipment in place. Its natural properties allow it to perform effectively while adhering to stringent regulations aimed at reducing harmful emissions. As businesses seek ways to comply with environmental standards, R290 shines as an excellent choice among the low GWP refrigerant list.
R32: A Versatile Option
R32 is another popular player in the realm of low-GWP refrigerants, boasting a GWP of 675—significantly lower than many traditional options like HFCs. This versatile option is suitable for a wide range of applications from residential air conditioning systems to commercial refrigeration setups. When comparing low GWP refrigerant vs GWP values, R32 stands out for its balance between performance and sustainability.
One notable advantage of R32 is its energy efficiency; it requires less energy to achieve optimal cooling compared to higher-GWP alternatives. This not only translates into lower operational costs but also supports initiatives aimed at energy conservation—an essential factor in today’s eco-conscious market. With ongoing advancements in technology and safety measures surrounding its use, R32 continues to gain traction as an ideal choice for modern refrigeration needs.
R454B: A Blend for the Future
R454B represents a new generation of blended low-GWP refrigerants designed specifically for use in commercial and residential applications alike. With a GWP rating around 466, this blend offers an excellent compromise between performance and environmental impact when placed alongside other options on the low GWP refrigerant list. Its composition allows it to work efficiently across various chillers while maintaining compliance with current regulations.
What sets R454B apart is its ability to provide effective cooling without compromising on safety or efficiency—making it an attractive option for businesses transitioning from higher-GWP alternatives. As industries work towards embracing more sustainable practices, this blend serves as a beacon of hope for future innovations in refrigeration technology. By choosing R454B or similar blends, businesses can align themselves with eco-friendly practices while still meeting operational demands.
Real-World Applications of Low-GWP Refrigerants

Low-GWP refrigerants are making waves across various sectors, proving that eco-friendly solutions can be both effective and efficient. From commercial refrigeration systems to residential air conditioning units, these alternatives are reshaping the landscape of cooling technologies. The transition to low GWP refrigerant options is not just a trend; it's a necessity for a sustainable future.
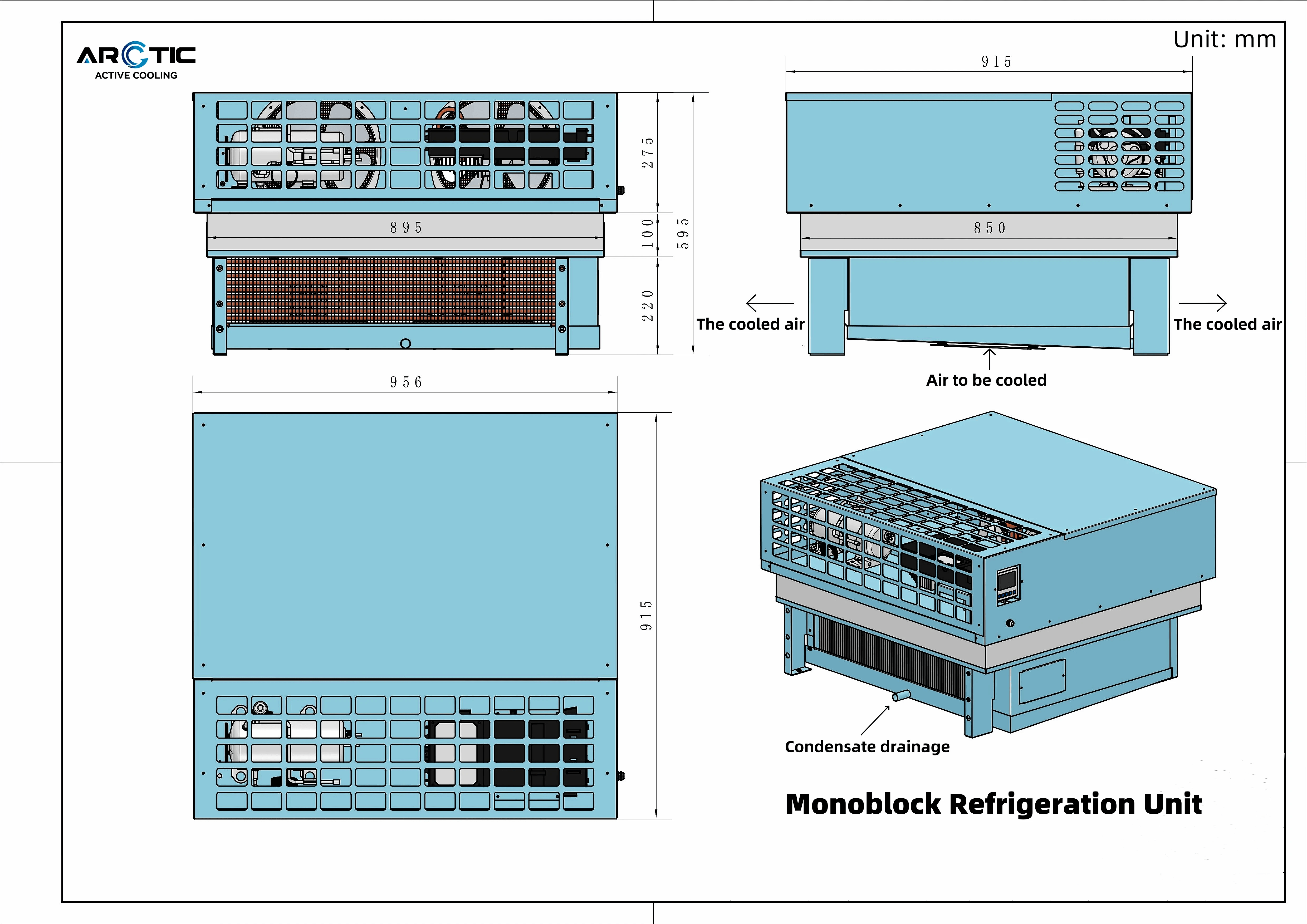
ARCTIC's Wall Mount Monoblocks
ARCTIC's wall mount monoblocks exemplify the application of low-GWP refrigerants in compact, efficient designs. These units utilize low GWP refrigerant chillers that ensure optimal cooling without contributing significantly to global warming potential. By choosing low GWP options, ARCTIC is not only enhancing energy efficiency but also adhering to environmental regulations and standards.
The benefits of these systems extend beyond sustainability; they offer impressive energy savings and lower operational costs for users. With the rising awareness of low GWP meaning in the context of climate change, consumers are increasingly leaning towards brands that prioritize eco-friendly practices. The innovative design and functionality of ARCTIC’s products showcase how businesses can thrive while championing sustainability.
Commercial Refrigeration Systems
In commercial settings, the shift toward low-GWP refrigerants is revolutionizing how businesses manage their refrigeration needs. Traditional systems often relied on high-GWP substances, which posed risks not only to the environment but also to compliance with evolving regulations. Low GWP refrigerant vs GWP comparisons highlight significant advantages in reducing greenhouse gas emissions while maintaining performance standards.
Moreover, many commercial refrigeration systems now integrate advanced technologies that leverage low GWP alternatives effectively. This transition helps businesses save on energy costs while meeting stringent regulatory requirements related to emissions and environmental impact. As more companies adopt these technologies, they contribute significantly to a greener economy and enhance their brand reputation among environmentally-conscious consumers.
Residential Air Conditioning
Residential air conditioning has also seen an influx of low-GWP refrigerants as homeowners become more aware of their environmental footprint. By replacing conventional high-GWP refrigerants with safer alternatives, residents can enjoy comfortable indoor climates without compromising on sustainability or safety concerns associated with harmful chemicals. The growing list of available low GWP refrigerant options provides homeowners with plenty of choices tailored to their specific needs.
The appeal doesn't stop at environmental benefits; many modern air conditioning units using low GWP refrigerants boast improved energy efficiency ratings as well as lower utility bills for homeowners over time. Additionally, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on ensuring that these new systems comply with safety standards related to flammability and toxicity—addressing common concerns about low GWP refrigerant safety head-on. With rising temperatures globally, investing in sustainable cooling solutions has never been more critical for both comfort and conscience.
Challenges in Transitioning to Low-GWP Refrigerants

Transitioning to low-GWP refrigerants is not without its hurdles. While the environmental benefits are clear, various challenges can impede widespread adoption. Understanding these challenges is crucial for stakeholders aiming to embrace low-GWP solutions effectively.
Initial Investment Costs
When comparing low GWP refrigerant vs GWP alternatives, the initial investment costs can be a significant barrier for many businesses. The upfront expenses associated with retrofitting existing systems or investing in new low GWP refrigerant chillers can deter organizations from making the switch. However, it's essential to consider that these investments often lead to long-term savings through energy efficiency and compliance with regulatory standards.
Technological Barriers to Adoption
Technological barriers also pose a challenge in the transition towards low GWP refrigerants. Many existing refrigeration systems were designed for high-GWP substances, making retrofitting or replacing them a complex process that requires specialized knowledge and equipment. Furthermore, not all low GWP refrigerants have been thoroughly tested across all applications, leading to uncertainties about performance and reliability.
Training and Education Needs
Lastly, training and education needs are paramount when it comes to adopting low GWP refrigerants safely and effectively. HVAC professionals must become familiar with the unique properties of various low GWP options on the low GWP refrigerant list, ensuring they understand safety protocols and handling procedures specific to each substance. Without proper education, there’s a risk of mishandling these eco-friendly alternatives, which could undermine their intended environmental benefits.
Conclusion
The journey towards sustainable refrigeration is not just a trend; it’s the future of our planet. As we continue to grapple with climate change, embracing low GWP refrigerants is essential for reducing our environmental impact. By prioritizing these alternatives, we can drive significant changes in how refrigeration systems operate and contribute to a healthier Earth.
The Future of Refrigeration Is Green
The future of refrigeration is undeniably green, marked by an increasing reliance on low GWP refrigerants that offer effective cooling without the hefty environmental price tag. Transitioning from traditional high-GWP options to low GWP alternatives not only curtails greenhouse gas emissions but also promotes energy efficiency across various sectors. With innovations in technology and growing regulatory support, the shift toward eco-friendly practices will redefine industry standards and consumer expectations alike.
Choosing the Right Low-GWP Refrigerant
Selecting the right low GWP refrigerant requires careful consideration of several factors, including application type, safety ratings, and efficiency levels. A comprehensive low GWP refrigerant list can guide businesses and consumers alike in making informed decisions—whether it’s for chillers or air conditioning systems. Understanding the nuances of low GWP meaning ensures that stakeholders choose options that align with their operational goals while minimizing their carbon footprint.
Embracing Eco-Friendly Practices for All
Embracing eco-friendly practices isn’t just a responsibility; it's an opportunity for innovation and growth within industries reliant on refrigeration technologies. As we educate ourselves about low GWP refrigerant safety and their applications in chillers, we pave the way for broader acceptance and implementation across markets. Ultimately, a collective commitment to sustainability will foster an environment where both businesses thrive and our planet flourishes.
