Introduction

"Arctic Active Cooling. Endless Possibilities. We capture new technologies in mobile and compact cooling. Full-size cooling in a miniature design, customized to make your device stand out with innovative thermal management."
In the world of refrigeration, understanding the various types of compressors is crucial for optimal performance and efficiency. Among these, the rotary refrigeration compressor stands out due to its unique design and functionality. But what is a rotary compressor in refrigeration? This introduction will guide you through the significance of selecting the right compressor for your needs and set the stage for a comparison between rotary and inverter compressors.
Understanding Refrigeration Compressor Types
Refrigeration compressors are essential components in cooling systems, responsible for compressing refrigerant gas and circulating it throughout the system. The two primary types—rotary compressors and inverter compressors—each have distinct features that cater to different applications. Understanding these differences can help you make informed decisions when choosing between them.
Importance of Choosing the Right Compressor
Selecting an appropriate compressor can significantly impact energy efficiency, performance, and overall operational costs of your cooling system. With numerous options available on the market, knowing which compressor is better: rotary or inverter can save both time and money in the long run. Properly assessing your specific needs ensures that you choose a solution that not only meets performance expectations but also aligns with energy-saving goals.
Overview of Rotary vs. Inverter Compressors
Rotary compressors utilize a rotating mechanism to compress refrigerant gas, making them compact and efficient for various applications like air conditioning systems or refrigerators. On the other hand, inverter compressors adjust their speed based on cooling demand, offering enhanced energy savings during operation; however, they may come at a higher initial cost compared to their rotary counterparts. As we delve deeper into this comparison throughout this guide, we will explore how do rotary compressors work? And examine key distinctions such as What is the difference between a rotary compressor and a normal compressor?
What is a Rotary Compressor?

When diving into the world of refrigeration, understanding the rotary refrigeration compressor is essential. This type of compressor is a key player in various cooling systems, providing efficient and reliable performance. But what exactly is a rotary compressor in refrigeration? Let’s break it down.
Definition and Functionality
A rotary compressor operates by using rotating mechanisms to compress refrigerant gas, transforming it into a high-pressure state for circulation through the cooling system. Unlike traditional compressors that rely on pistons, rotary compressors utilize either rolling or sliding elements to achieve compression. This design not only enhances efficiency but also allows for smoother operation, making them popular in both residential and commercial applications.
Key Features of Rotary Compressors
Rotary compressors are renowned for their compact size and lightweight design, which makes them ideal for space-constrained installations. They often feature low noise levels during operation, thanks to their continuous motion mechanics that reduce vibrations significantly compared to other types of compressors. Additionally, these compressors typically exhibit excellent energy efficiency ratings, which can lead to lower operational costs over time—an important consideration when evaluating rotary compressor vs inverter compressor options.
Common Applications and Industries
You’ll find rotary refrigeration compressors widely used in various applications ranging from air conditioning units to refrigerators and freezers in both domestic and industrial settings. Their ability to handle varying load conditions makes them suitable for diverse environments such as restaurants, supermarkets, and HVAC systems in office buildings. In fact, if you look at a rotary compressor diagram, you’ll see how its straightforward design lends itself well to these widespread applications while ensuring reliability and performance.
How Do Rotary Compressors Work?

Rotary compressors are a fascinating piece of engineering in the world of refrigeration. To truly grasp how they function, it's essential to delve into their basic principles, components, and performance metrics. Understanding these aspects will help clarify why rotary refrigeration compressors are often favored in various applications.
Basic Working Principles
At the heart of any rotary compressor's operation is its ability to compress refrigerant gas efficiently. The fundamental principle revolves around the rotation of one or more blades within a cylinder, which compresses the refrigerant as it moves through the system. This process not only raises the pressure but also facilitates heat exchange, making it integral to cooling systems.
So, what is a rotary compressor in refrigeration? It’s essentially a device that uses rotary motion to achieve compression, differing significantly from traditional piston-based designs. In this way, rotary compressors can offer smoother operation and reduced vibrations compared to normal compressors.
Components of a Rotary Compressor
A typical rotary compressor consists of several key components that work harmoniously to ensure efficient performance. The main parts include the rotor, housing, and motor; each plays an essential role in maintaining functionality and efficiency. The rotor rotates within a cylindrical chamber, compressing refrigerant gas against the walls as it moves.
Additionally, lubrication systems are critical for reducing friction and wear on moving parts within the rotary compressor. This lubrication not only enhances longevity but also contributes to quieter operation—a significant advantage over many other types of compressors. When exploring a rotary compressor diagram, you’ll notice how these components interact seamlessly for optimal performance.
Efficiency and Performance Metrics
When discussing efficiency in terms of rotary vs inverter compressor technologies, it’s crucial to consider energy consumption and operational effectiveness under varying loads. Rotary refrigeration compressors typically excel at maintaining consistent performance levels while consuming less energy compared to traditional models—especially in moderate load situations.
Performance metrics such as Coefficient of Performance (COP) can be used to evaluate how effectively these compressors convert electrical energy into cooling output. Many users find that selecting between a rotary compressor vs inverter compressor in AC applications often boils down to specific usage requirements and operational costs over time.
In summary, understanding how do rotary compressors work involves recognizing their unique design features and operational efficiencies that set them apart from conventional options on the market today.
Rotary Compressor vs. Inverter Compressor

When it comes to choosing between a rotary compressor and an inverter compressor, understanding their energy efficiency is crucial. A rotary refrigeration compressor typically operates at a fixed speed, which can lead to less energy efficiency compared to inverter models that adjust their speed based on cooling demand. This flexibility in inverter compressors often results in lower energy consumption and operational costs over time.
Comparison of Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is one of the most significant factors when evaluating rotary vs. inverter compressors. The rotary compressor, while reliable and effective for many applications, usually consumes more power due to its constant operational speed, especially during low-load conditions. On the other hand, inverter compressors adapt their output according to the cooling needs, allowing for substantial savings on electricity bills—making them a popular choice for energy-conscious consumers.
Performance in Varying Loads
Performance under varying loads is another area where these two types of compressors diverge significantly. Rotary compressors excel in stable environments where the cooling load remains consistent; they deliver solid performance without much fluctuation. However, when faced with fluctuating demands—like those often seen in residential air conditioning—an inverter compressor shines by modulating its capacity to maintain optimal temperatures efficiently.
Use Cases for Each Type
Understanding specific use cases can also help clarify the differences between rotary and inverter compressors. For instance, a rotary compressor example might include small refrigerators or commercial refrigeration units where space constraints are critical and consistent load is expected. Meanwhile, an inverter compressor is frequently found in modern air conditioning systems designed for homes and offices that experience variable loads throughout the day; this adaptability makes it ideal for such applications.
Advantages of Rotary Refrigeration Compressors
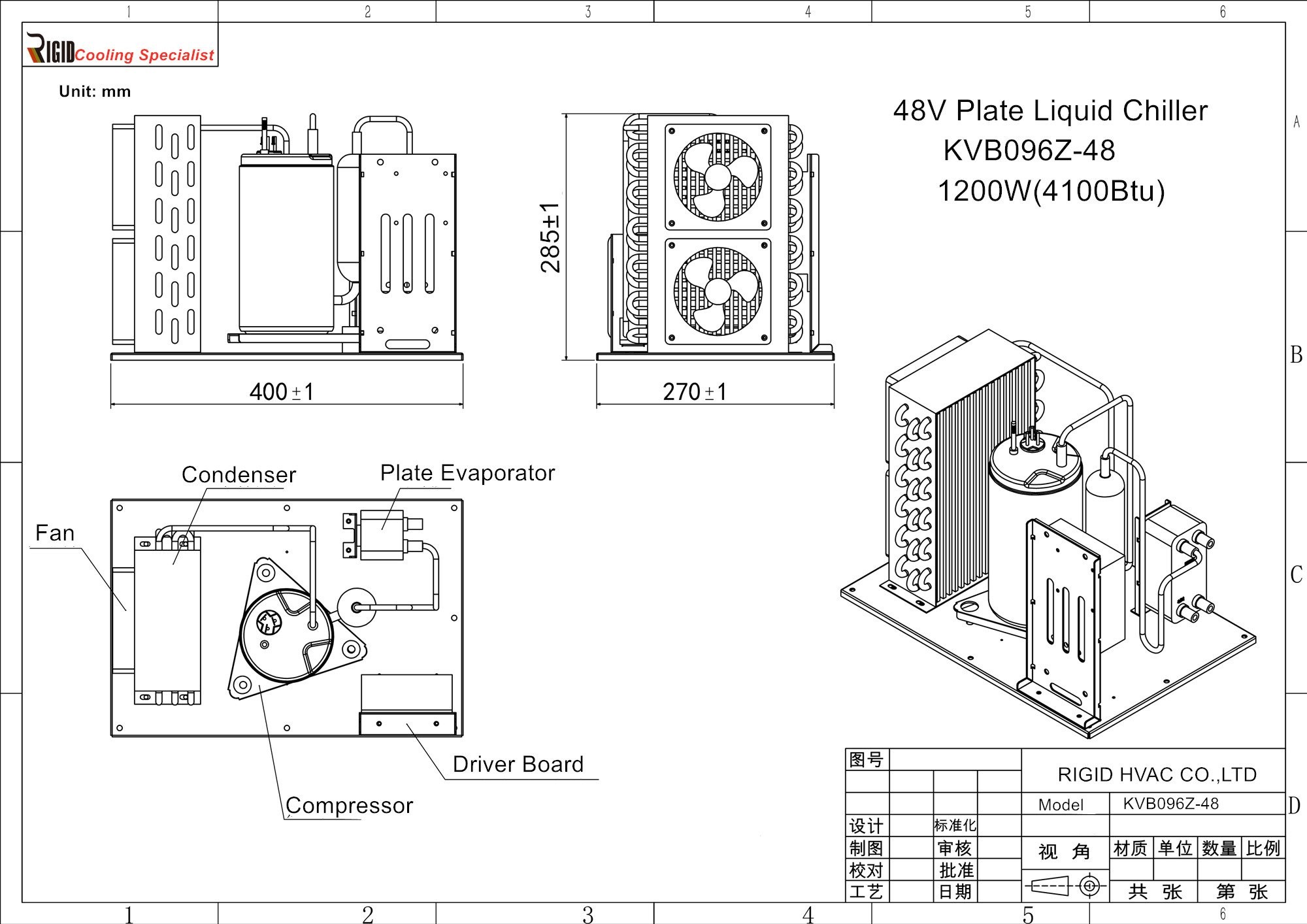
Rotary refrigeration compressors are gaining popularity for a variety of reasons that make them stand out in the crowded field of refrigeration options. Their design and functionality offer unique benefits that can enhance efficiency and performance in various applications. Let’s delve into some key advantages that make rotary compressors a preferred choice for many.
Space and Weight Efficiency with ARCTIC
One of the standout features of rotary refrigeration compressors is their space and weight efficiency, particularly highlighted by innovations like ARCTIC technology. These compressors are compact, allowing for installation in tighter spaces without sacrificing performance. This is especially beneficial in residential air conditioning units or commercial refrigeration systems where available space is often at a premium.
The lightweight design also means easier handling during installation, which can save both time and labor costs. In settings where every square inch counts, understanding what is a rotary compressor in refrigeration becomes crucial to maximizing space utility. With their efficient footprint, rotary compressors can fit seamlessly into various designs while still delivering robust cooling power.
Noise Reduction Benefits
Another significant advantage of rotary compressors lies in their noise reduction capabilities compared to traditional models. The operation of these compressors tends to be quieter due to their smooth rotational motion; this makes them ideal for residential settings where noise levels are a concern. When evaluating which compressor is better—rotary or inverter—noise reduction often becomes a deciding factor for consumers who prioritize comfort.
The reduced noise not only contributes to a more pleasant indoor environment but also enhances the overall user experience when using appliances such as air conditioners or refrigerators equipped with rotary technology. Understanding how do rotary compressors work helps appreciate why they operate more quietly than conventional options, providing an added layer of appeal for homeowners and businesses alike.
Reliability and Maintenance Considerations
Reliability is paramount when it comes to choosing any refrigeration system, and rotary compressors excel in this area as well. They have fewer moving parts compared to traditional reciprocating models, leading to lower wear and tear over time, thus enhancing durability and lifespan. This reliability translates into less frequent maintenance needs—a significant advantage when considering the total cost of ownership over time.
Moreover, understanding the difference between a rotary compressor and a normal compressor reveals why users might prefer the former: they typically require less intervention from technicians due to their robust design features. Regular maintenance checks become simpler too; knowing how do rotary compressors work allows technicians to quickly identify any potential issues without extensive downtime or complicated repairs.
In summary, whether you're looking at specific applications like rotary compressor example installations or analyzing technical details via a rotary compressor diagram, it's clear that these machines offer compelling advantages worth considering.
Selecting the Right Compressor for Your Needs

Choosing the right compressor for your refrigeration system can feel like navigating a maze of options, especially when considering rotary refrigeration compressors and their inverter counterparts. The decision hinges on various factors such as efficiency, application, and performance requirements. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed choice that meets your specific needs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing
When pondering What is a rotary compressor in refrigeration?, it's essential to assess your cooling requirements first. Consider the size of the space you're cooling, as well as the temperature ranges you need to maintain. Additionally, energy efficiency plays a crucial role; you'll want a compressor that not only performs well but also saves you money on utility bills over time.
Next, evaluate whether you need a consistent output or if variable performance is acceptable. This leads us into the debate of Which compressor is better: rotary or inverter? Rotary compressors excel in steady-state applications, while inverter compressors adapt to varying load conditions effectively. Lastly, don’t overlook maintenance and reliability; choosing a robust option can save headaches down the road.
Rotary Compressor Examples in Real Applications
Rotary compressors are widely used across various industries due to their versatility and efficiency. For instance, they are commonly found in residential air conditioning systems where space is at a premium—think compact units that fit neatly into tight spots without sacrificing performance. Another classic example includes commercial refrigeration systems used in restaurants and supermarkets where consistent cooling is critical.
In industrial applications, rotary compressors are often employed for process cooling or HVAC systems because they handle larger volumes efficiently while maintaining low noise levels—a significant advantage in environments where sound matters. These examples highlight how rotary refrigeration compressors cater to diverse needs while ensuring reliable operation under different conditions.
Analyzing the Rotary Compressor Diagram
To truly grasp how do rotary compressors work?, examining a rotary compressor diagram can be incredibly enlightening. A typical diagram showcases key components such as the rotor assembly, motor section, and discharge outlet—all working harmoniously to compress refrigerant gas efficiently. By visualizing these parts' interactions, one can appreciate how this technology differs from traditional options.
The diagram also illustrates airflow paths and pressure changes within the system—critical information for understanding what sets rotary compressors apart from normal compressors. In essence, this visual representation demystifies complex processes and helps clarify What is the difference between a rotary compressor and a normal compressor? Ultimately, it becomes clear how each component contributes to overall efficiency and performance metrics vital for effective cooling solutions.
Conclusion
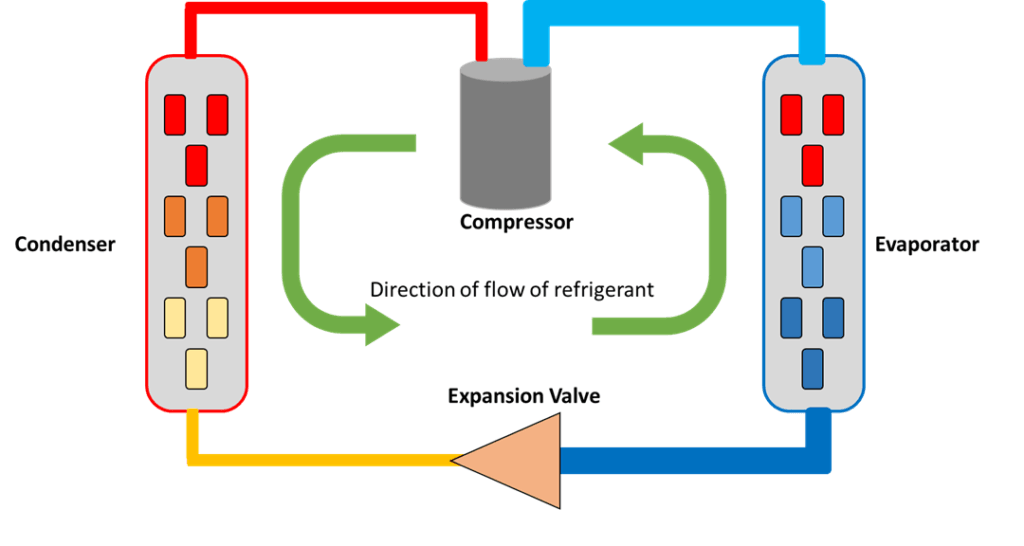
In summary, understanding the nuances of various compressor types is crucial for anyone involved in refrigeration systems. The rotary refrigeration compressor stands out for its efficiency and reliability, making it a popular choice across multiple industries. By weighing the advantages of rotary versus inverter compressors, one can make informed decisions that align with specific operational needs.
Key Takeaways on Compressor Selection
When selecting a compressor, it's essential to consider factors such as energy efficiency, load variability, and application suitability. The question What is a rotary compressor in refrigeration? highlights its unique design and functionality that cater to diverse cooling requirements. Additionally, knowing Which compressor is better: rotary or inverter? boils down to understanding your specific demands; both have distinct advantages depending on the context.
Future Trends in Refrigeration Compressors
The future of refrigeration compressors leans toward enhanced energy efficiency and smart technology integration. Innovations are emerging that will further improve the performance metrics of rotary compressors while reducing their environmental impact. As industries continue to evolve, expect advancements that refine how we understand How do rotary compressors work? and push for even greater efficiency in applications like air conditioning.
Making Informed Choices for Efficiency
Making informed choices about compressors means not only understanding their mechanics but also analyzing real-world applications—like using a Rotary compressor example to visualize its benefits effectively. By examining the Rotary compressor diagram, users can grasp how these systems operate internally and what sets them apart from traditional options. Ultimately, whether you lean towards a rotary or inverter model, prioritizing efficiency will lead you towards more sustainable practices in refrigeration.
