Introduction
"Arctic Active Cooling. Endless Possibilities. We capture new technologies in mobile and compact cooling. Full-size cooling in a miniature design, customized to make your device stand out with innovative thermal management."
In the realm of refrigeration, defrosting is a critical process that ensures optimal performance and efficiency. Without proper defrosting techniques, ice buildup can severely hinder the functionality of refrigeration systems, leading to increased energy consumption and potential equipment failure. Among various methods available, hot gas defrost stands out as an effective solution for maintaining the integrity of refrigeration units.
Understanding Defrosting in Refrigeration
Defrosting in refrigeration refers to the process of removing accumulated frost or ice from evaporator coils. This buildup can restrict airflow and reduce cooling efficiency, making it essential to implement effective defrost methods. Understanding how hot gas defrost works provides insight into one of the most efficient ways to keep refrigeration systems running smoothly.
The Importance of Efficient Defrost Methods
Efficient defrost methods are crucial for minimizing downtime and maximizing operational efficiency in refrigeration systems. When considering options like hot gas defrost versus electric heating elements, it's vital to evaluate which process will be done during hot gas defrosting for optimal results. By choosing an effective method, businesses can reduce energy costs and improve overall system reliability.
Overview of Hot Gas Defrost Techniques
Hot gas defrost techniques utilize heated refrigerant gases to melt away frost build-up on evaporator coils quickly and effectively. This method involves several components working together, including a hot gas defrost valve that regulates the flow of heated refrigerant during the cycle. As we delve deeper into this topic, we will explore key aspects such as whether the compressor runs during hot gas defrost and how temperature control affects efficiency.
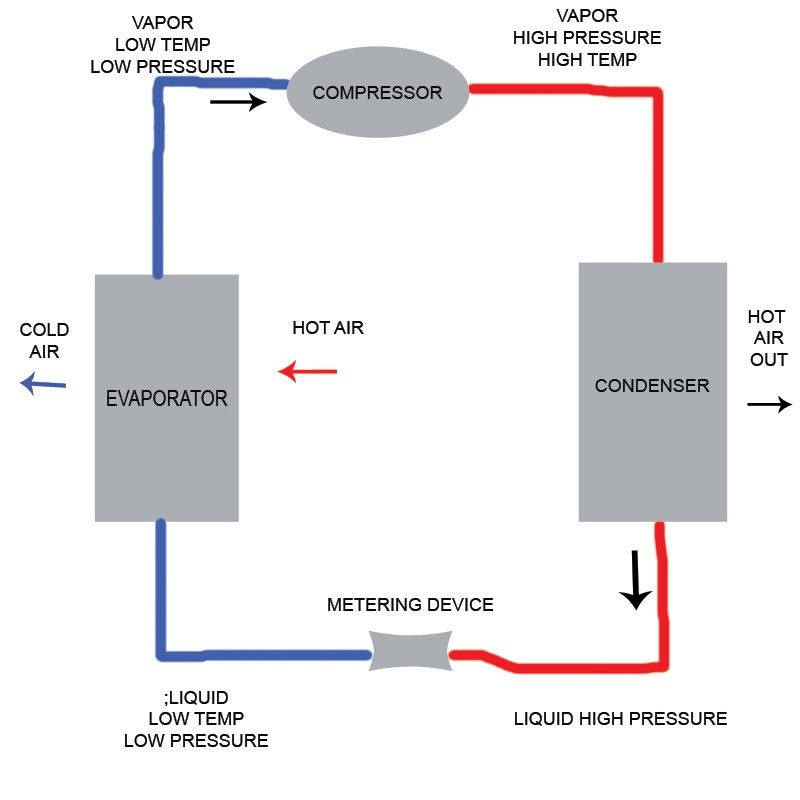
What is Hot Gas Defrost?
Hot gas defrost is a specialized method used in refrigeration systems to remove frost buildup from evaporator coils. This process utilizes the heat generated by refrigerant gas, which is redirected from the compressor during specific cycles. By efficiently managing this heat, hot gas defrost ensures that refrigeration units operate smoothly and maintain optimal temperatures.
Definition and Process
In essence, hot gas defrosting involves circulating heated refrigerant gas through the evaporator coils to melt accumulated frost or ice. When the system detects that frost has formed, it activates the hot gas defrost cycle, diverting warm refrigerant from the compressor to the coils. During this process, which typically lasts between 5 to 30 minutes depending on conditions, any ice present is melted away, restoring efficiency and preventing operational issues.
Key Components of Hot Gas Defrost
Several critical components work together in a hot gas defrost system to ensure its effectiveness. The primary element is the **hot gas defrost valve**, responsible for controlling the flow of heated refrigerant into the evaporator during defrost cycles. Additionally, there are temperature sensors that monitor conditions within the refrigeration unit and trigger defrost cycles as needed, ensuring timely intervention before excessive frost can hinder performance.
Advantages of Hot Gas Defrost Systems
Hot gas defrost systems offer several benefits compared to traditional electric heating methods. First and foremost, they provide faster and more efficient defrosting by utilizing existing heat from refrigerant instead of relying on external power sources—this directly leads to reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs. Furthermore, since these systems don't require additional heating elements or electrical components for each cycle, they often involve less maintenance while enhancing overall reliability in various applications like commercial refrigeration setups.
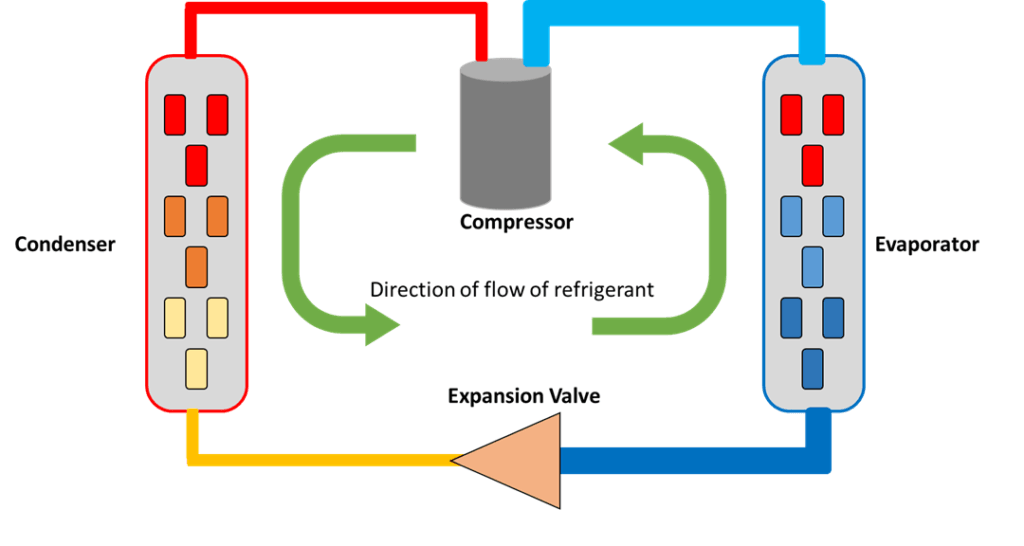
Hot Gas Defrost Cycle Explained
The hot gas defrost cycle is a vital process in refrigeration systems that helps maintain optimal performance by removing frost buildup. This cycle utilizes hot refrigerant gas to melt ice and frost that accumulates on evaporator coils, ensuring efficient heat exchange. Understanding the intricacies of this cycle is essential for anyone involved in refrigeration technology.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Cycle
The hot gas defrost cycle begins when the system detects excessive frost accumulation on the evaporator coils, triggering a switch to initiate the defrost process. During this phase, hot refrigerant gas is diverted from the compressor through a dedicated hot gas defrost valve, allowing it to flow into the evaporator coils. This heated gas raises the temperature of the coils, effectively melting any accumulated frost and restoring airflow.
Once the frost has melted, water drains away from the evaporator, and normal refrigeration resumes as the system returns to its cooling mode. It’s important to note that during this process, some components may continue running while others pause temporarily—this brings us to another critical question: does the compressor run during hot gas defrost? The answer varies by design but often involves strategic operation to maximize efficiency while minimizing energy consumption.
Hot Gas Defrost Valve Functionality
The hot gas defrost valve plays a crucial role in regulating how and when hot refrigerant enters the evaporator during a defrost cycle. This valve controls flow direction; when activated, it directs high-pressure vapor from the compressor into specific sections of the system designated for warming up during defrosting. Its precise functionality ensures that only necessary areas receive heat while maintaining overall system efficiency.
Understanding what are the differences between electric and hot gas defrost cycles helps clarify why many facilities prefer this method for certain applications. While electric heating can be effective, it often consumes more energy compared to utilizing existing refrigerant gases—making hot gas systems more economical in many cases.
Common Applications in Refrigeration
Hot gas defrost systems are widely used across various refrigeration applications due to their efficiency and effectiveness at preventing ice buildup on critical components. You'll commonly find them in commercial freezers, walk-in coolers, and industrial chillers where consistent temperature control is paramount for product preservation. These systems not only enhance operational performance but also reduce maintenance costs associated with manual thawing or less efficient electric alternatives.
In summary, understanding how these processes work—including which processes will be done during hot gas defrosting—can significantly impact your choice of refrigeration technology for specific needs or environments.
Electric vs. Hot Gas Defrost: Key Differences
When it comes to defrosting methods in refrigeration, electric and hot gas defrost cycles are the two main contenders, each with its own approach and benefits. So, what are the differences between electric and hot gas defrost cycles? Electric defrosting typically involves heating elements that melt ice buildup, while hot gas defrost utilizes refrigerant vapor from the compressor to warm up and clear frost from evaporator coils. This fundamental difference shapes how each system operates and impacts efficiency.
What are the Differences Between Electric and Hot Gas Defrost Cycles?
Electric defrost systems rely on resistance heaters that generate heat to combat frost accumulation, which can lead to higher energy consumption during operation. In contrast, hot gas defrost cycles use the heat generated by compressing refrigerant gases—essentially harnessing waste heat for a more efficient process. Additionally, while electric systems may require periodic manual intervention for maintenance or troubleshooting, hot gas defrost typically integrates seamlessly into existing refrigeration cycles without extra steps.
Performance Comparison
In terms of performance, hot gas defrost has distinct advantages over electric systems. The hot gas defrost cycle is often faster because it uses heated refrigerant directly from the compressor rather than waiting for electrical elements to warm up. Moreover, does the compressor run during hot gas defrost? Yes! This continuous operation ensures that there’s minimal interruption in cooling performance while effectively managing frost buildup.
Cost Considerations
Cost is always a significant factor when comparing these two methods of refrigeration management. While electric systems may have lower initial installation costs due to simpler components like heating elements, they can lead to higher operational costs over time because of increased energy consumption during each cycle. On the other hand, though the upfront investment for a hot gas defrost system might be steeper due to additional components like a hot gas defrost valve and modifications to existing compressors, long-term savings can be realized through improved energy efficiency and reduced maintenance needs.
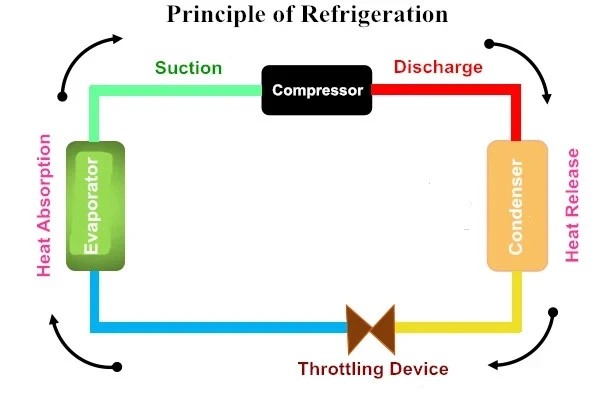
The Role of the Compressor
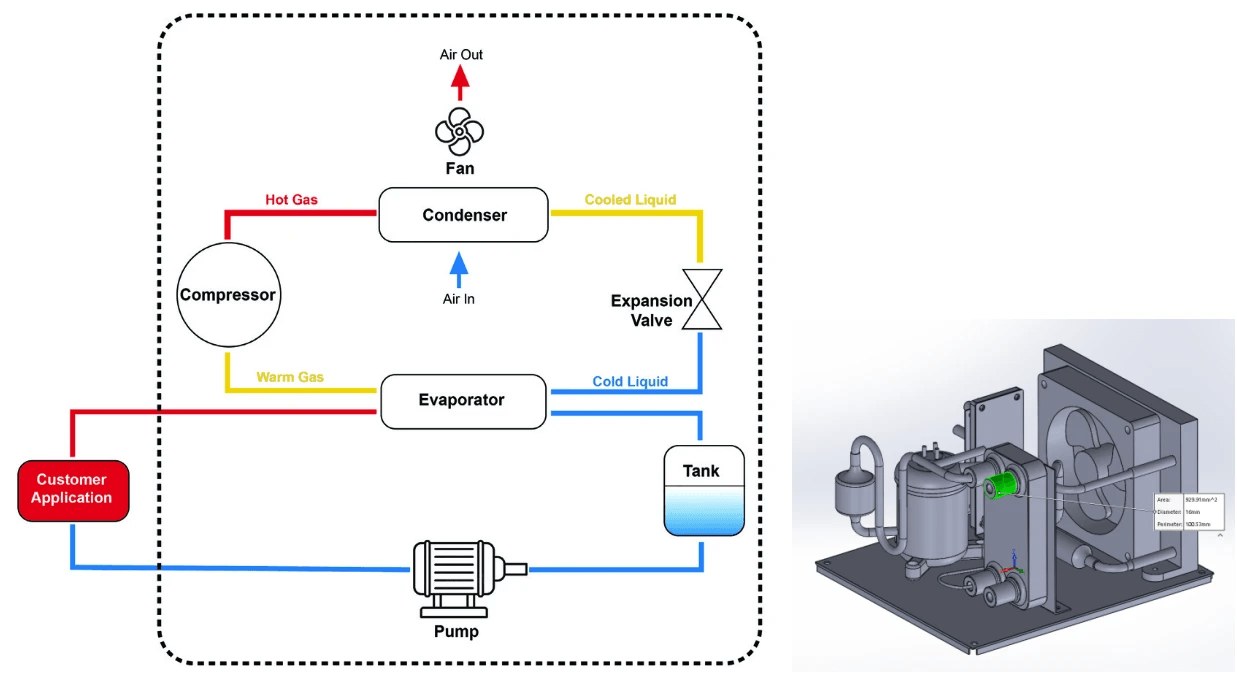
In any refrigeration system, the compressor plays a pivotal role, especially during the hot gas defrost cycle. Understanding how it interacts with the rest of the system can clarify why hot gas defrosting is often preferred over electric methods. Let's dive into how this key component functions during defrosting and its implications for overall efficiency.
Does the Compressor Run During Hot Gas Defrost?
Yes, the compressor does run during hot gas defrost. This is a fundamental aspect that differentiates hot gas defrost from other methods, such as electric defrost cycles. While some systems may shut down their compressors to initiate an electric heating process, in hot gas defrost refrigeration, the compressor continues to operate and circulate refrigerant through the hot gas defrost valve to effectively melt away frost buildup.
Impact on System Efficiency
The operation of the compressor during hot gas defrost directly influences system efficiency. By keeping the compressor running, energy consumption remains relatively stable compared to systems that require additional electrical heating elements for defrosting. This not only enhances performance but also contributes to a more consistent temperature control within the refrigeration unit—key for maintaining optimal conditions and reducing operational costs.
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
To ensure your compressor operates efficiently during hot gas defrost cycles, regular maintenance is essential. Checking refrigerant levels and ensuring proper lubrication helps prevent wear and tear on this critical component. Additionally, monitoring your hot gas defrost temperature settings can help identify any irregularities early on—keeping your system performing at its best while minimizing downtime.
Temperature Control in Hot Gas Defrost
Temperature control is a critical aspect of hot gas defrost systems, ensuring that the defrost cycle operates efficiently and effectively. The ability to maintain optimal temperatures not only enhances the performance of the hot gas defrost cycle but also prolongs the lifespan of refrigeration equipment. Understanding how temperature specifications influence the process is essential for anyone involved in refrigeration management.
Hot Gas Defrost Temperature Specifications
Hot gas defrost temperature specifications typically range between 30°F to 60°F (about -1°C to 15°C), depending on the system design and application requirements. These temperatures are crucial because they determine how effectively ice buildup is melted during the hot gas defrost cycle. Keeping track of these specifications helps ensure that the hot gas defrost valve operates correctly, allowing for efficient heat transfer and optimal system performance.
Maintaining appropriate temperatures during hot gas defrosting not only aids in melting frost but also prevents overheating, which could damage components within the refrigeration system. Therefore, operators must be vigilant about adhering to these temperature guidelines, which can vary based on specific models and manufacturer recommendations. Proper calibration of temperature settings ensures that systems run smoothly without unnecessary interruptions or failures.
Monitoring and Adjusting Temperature Settings
Monitoring temperature settings in a hot gas defrost refrigeration system is vital for achieving consistent performance. Operators often utilize advanced digital controllers equipped with sensors to keep an eye on current temperatures throughout the hot gas defrost cycle. This real-time monitoring allows for quick adjustments if temperatures deviate from established parameters.
Adjustments may be necessary due to external factors such as ambient temperature changes or variations in load conditions within the refrigeration unit itself. If temperatures are too low, ice may not melt efficiently; conversely, excessively high temperatures can lead to energy wastage or even damage to sensitive components. Thus, understanding how to monitor and adjust these settings is key to maintaining an effective hot gas defrost process.
Effects of Temperature on Defrosting Efficiency
The efficiency of a hot gas defrost cycle heavily relies on maintaining proper temperature levels throughout its operation. If temperatures are set too low during hot gas defrosting, it can lead to incomplete melting of frost or ice buildup—ultimately affecting overall cooling performance and increasing energy costs due to extended run times. Conversely, excessively high temperatures can lead not only to wasted energy but also potential damage within critical components like evaporators.
Moreover, achieving optimal temperatures enhances heat exchange efficiency through the hot gas defrost valve, ensuring that warm refrigerant effectively melts any accumulated frost or ice quickly and thoroughly. This balance between efficiency and effectiveness is what makes mastering temperature control so crucial in modern refrigeration systems utilizing hot gas methods over electric alternatives—especially when considering what are the differences between electric and hot gas defrost cycles?
In summary, effective monitoring and control of temperatures during a hot gas defrost cycle directly impact both operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in refrigeration systems.
Conclusion

In the world of refrigeration, choosing the right defrost system can make all the difference in efficiency and performance. Hot gas defrost systems stand out due to their rapid and effective defrosting capabilities, ensuring that your refrigeration units run smoothly without excessive downtime. With a deeper understanding of hot gas defrost, one can appreciate its benefits over traditional methods like electric defrosting.
Why Choose Hot Gas Defrost Systems
One of the primary reasons to choose hot gas defrost systems is their speed and efficiency in melting away frost build-up. Unlike electric systems that may take longer and consume more energy, hot gas defrost cycles utilize heated refrigerant to quickly eliminate ice, ensuring optimal performance without sacrificing energy consumption. Additionally, during hot gas defrosting, the compressor continues to operate effectively, maintaining system pressure and improving overall efficiency.
Moreover, hot gas defrost valves play a crucial role in controlling this process by directing heated refrigerant where it’s needed most. This targeted approach not only enhances the speed of the cycle but also reduces wear on components compared to electric methods. Ultimately, adopting a hot gas defrost refrigeration system translates into lower operational costs and improved reliability.
Future Trends in Defrost Technology
As technology advances, we can expect innovations that further enhance the efficiency of hot gas defrost systems. Future developments may focus on smarter temperature control mechanisms that optimize hot gas defrost temperature settings automatically based on environmental conditions or usage patterns. Such advancements will ensure that these systems remain at the forefront of energy-efficient refrigeration solutions.
Additionally, integrating IoT (Internet of Things) technology could allow for real-time monitoring of the hot gas defrost cycle, providing valuable insights for maintenance and operational adjustments. This shift towards automation will not only streamline processes but also enhance user experience by reducing manual intervention requirements during critical phases like hot gas defrosting.
Furthermore, as industries strive for sustainability, future trends may see an increased emphasis on eco-friendly refrigerants within these systems to minimize environmental impact while maintaining high performance levels during processes such as hot gas defrosting.
ARCTIC's Innovations in Refrigeration Solutions
At ARCTIC, we pride ourselves on leading the charge in innovative refrigeration solutions tailored for modern demands. Our latest offerings incorporate advanced features designed specifically for optimizing hot gas defrost cycles while ensuring minimal energy consumption and maximum reliability throughout operation periods—especially during critical moments when frost removal is essential.
We understand that questions like Does the compressor run during hot gas defrost? are common among users looking for clarity about their systems' operations; thus our designs prioritize seamless functionality with clear indicators for maintenance needs based on real-time data analysis from our smart monitoring tools.
With ARCTIC's commitment to innovation and excellence in refrigeration technology—combined with our expertise in enhancing processes like those found within a typical hot gas defrost cycle—we are dedicated to providing solutions that redefine industry standards while prioritizing customer satisfaction every step of the way.
