Introduction
"Arctic Active Cooling. Endless Possibilities. We capture new technologies in mobile and compact cooling. Full-size cooling in a miniature design, customized to make your device stand out with innovative thermal management."
Understanding the Basics of Cooling
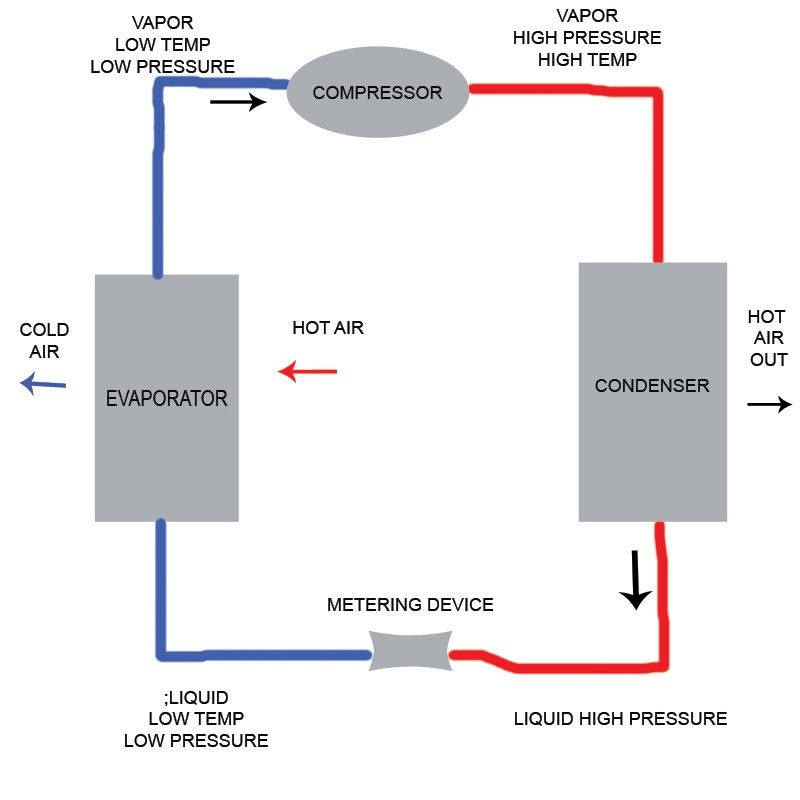
Air conditioning systems are designed to regulate indoor temperatures by removing heat from the air. At the heart of these systems lie two essential components: the air conditioner condenser and the compressor. Understanding how these parts interact is vital for anyone looking to enhance their cooling experience, whether at home or in industrial settings.
Key Functions of AC Systems
The primary function of an AC system is to maintain a comfortable environment by controlling temperature and humidity levels. The compressor pumps refrigerant through the system, while the condenser releases heat outside, making them integral to efficient cooling processes. Knowing how these components work together helps clarify why choosing between a central condenser vs compressor can impact overall performance significantly.
Importance of Choosing Between Systems
Selecting between an air conditioner condenser vs compressor can have lasting effects on energy efficiency and operational costs. Each component has its unique advantages and potential drawbacks that can influence your decision based on specific needs or industry applications. Additionally, understanding AC compressor condenser price points and replacement costs can guide you toward making financially sound choices for your cooling solutions.
Defining Condenser and Compressor

What is an Air Conditioner Condenser?
An air conditioner condenser is a vital part of any cooling system, responsible for releasing heat absorbed from inside your home to the outside environment. It typically consists of coils that allow refrigerant gas to cool down and condense back into a liquid state after it has absorbed heat indoors. This process is crucial for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature, making the air conditioner condenser an indispensable player in your HVAC setup.
In essence, when you're comparing air conditioner condenser vs compressor functionalities, remember that the former focuses on expelling heat while facilitating refrigerant transformation. If your AC isn’t cooling properly, it might be time to inspect this component for any signs of wear or damage. So if you find yourself sweating buckets in July, don’t forget about that poor little condenser working hard outside!
Understanding the Role of a Compressor
The compressor acts like the heart of your air conditioning system—it pumps refrigerant throughout the system while increasing its pressure and temperature in the process. Essentially, it takes low-pressure gas from the evaporator coil (where cooling occurs) and compresses it into high-pressure gas before sending it off to the condenser for heat release. Without a functioning compressor, your cooling system would be as effective as a chocolate teapot.
In discussions about AC compressor and condenser replacement costs, it's important to note that issues with either part can lead to inefficient operation or complete failure of your AC unit. The compressor's role in regulating refrigerant flow makes it pivotal not just in keeping cool but also in ensuring energy efficiency across your HVAC system. So when considering central condenser vs compressor dynamics, remember: both are essential yet serve distinct purposes.
Differences in Functionality
While both components are integral to an air conditioning system’s performance, their functionalities are distinctly different—like apples and oranges! The primary difference lies in their roles; while condensers focus on releasing heat from refrigerants outside your home, compressors work tirelessly to circulate that refrigerant through various phases within the AC unit itself.
When you think about compressor vs condenser vs evaporator interactions within an HVAC setup, it's clear each has unique responsibilities contributing to overall efficiency and comfort levels indoors. For instance, if you’re facing issues with airflow or temperature regulation at home, pinpointing whether it's due to a faulty compressor or ineffective condenser can save you time—and money—in repairs or replacements down the line! Understanding these differences will empower homeowners when faced with decisions regarding maintenance or upgrades.
How Each Component Works

Understanding how the air compressor and condenser function is crucial for anyone looking to optimize their cooling systems. The interplay between these components defines the efficiency and effectiveness of air conditioning units. Let’s delve into the mechanisms that make them tick.
Mechanism of an Air Compressor Condenser
The air compressor condenser works by taking in refrigerant gas from the compressor, which has been compressed at high pressure and temperature. As this gas enters the condenser, it cools down and changes state from a gas to a liquid, releasing heat in the process. This phase change is essential for efficient cooling, as it allows the system to circulate refrigerant effectively throughout your AC unit.
In terms of mechanics, the air compressor condenser relies on a series of coils and fans to enhance heat exchange. The fan blows ambient air over these coils, facilitating rapid cooling of the refrigerant inside. This process is where we see a clear distinction in functionality when comparing an air conditioner condenser vs compressor.
The Operation of a Central Condenser
A central condenser operates on similar principles but serves larger spaces or multiple zones within buildings. It collects refrigerant from various evaporators spread throughout different rooms or areas, allowing for centralized temperature control. By efficiently managing large volumes of refrigerant, central condensers can significantly enhance overall system performance compared to standalone units.
In operation, central condensers utilize larger coils and more powerful fans than typical AC systems to handle increased loads effectively. These components work together seamlessly to ensure that cooled liquid refrigerant is sent back to compressors or evaporators without losing efficiency along the way. When discussing central condenser vs compressor setups, it's vital to consider how they integrate into broader HVAC systems for optimal performance.
Efficiency Levels in Compressor vs Condenser
When evaluating efficiency levels between compressors and condensers, it's essential first to understand their distinct roles within an HVAC system. Compressors are primarily responsible for increasing pressure and temperature in order to facilitate heat transfer; however, they consume significant energy during this process. In contrast, condensers focus on dissipating heat while converting gaseous refrigerants back into liquids with less energy expenditure.
Efficiency metrics can vary widely based on design quality and operational conditions; thus comparing AC compressor condenser price alongside their efficiency ratings can reveal valuable insights for consumers seeking cost-effective solutions. Additionally, understanding potential ac compressor and condenser replacement costs helps homeowners plan better for long-term maintenance investments without compromising performance levels over time. Ultimately, when you weigh compressor vs condenser vs evaporator roles carefully within your system's architecture, you can make informed decisions that lead toward enhanced energy savings and overall comfort.
Applications in Different Industries

Use Cases in Medical and Aerospace
In the medical field, precision is paramount; thus, reliable cooling systems are crucial for equipment such as MRI machines and surgical devices. In this context, the air conditioner condenser vs compressor discussion becomes significant because both components contribute to maintaining optimal operational temperatures. Aerospace also relies heavily on these systems to ensure that sensitive instruments function correctly at high altitudes where temperature fluctuations can be extreme.
The air compressor condenser plays a vital role in both industries by ensuring that equipment remains cool under pressure. For instance, medical imaging devices need consistent cooling to avoid overheating during prolonged use—this is where an efficient AC compressor condenser shines. In aerospace applications, central condensers are often paired with compressors to create robust climate control systems that can withstand varied atmospheric conditions while ensuring safety and reliability.
Food Industry Cooling Solutions
Here, the choice between a central condenser vs compressor often hinges on space constraints and energy efficiency requirements. Refrigeration units must utilize both components effectively to keep perishables at safe temperatures while minimizing energy costs.
AC compressors work alongside condensers in commercial refrigeration systems found in grocery stores or restaurants, ensuring rapid cooling without compromising food quality. The air conditioner condenser vs compressor debate extends here too; understanding how each functions helps businesses optimize their operations while keeping an eye on AC compressor and condenser replacement costs when repairs are needed. With proper maintenance strategies tailored for these units, businesses can extend their longevity significantly.
Automotive Applications of Compressors
In the automotive world, compressors play an essential role in vehicle air conditioning systems—making them indispensable for comfort during hot weather drives. The comparison of compressor vs condenser vs evaporator becomes particularly relevant here as all three components work together seamlessly to provide efficient cabin cooling for passengers. Understanding how these elements interact helps manufacturers design more effective automotive climate control systems.
Moreover, considering the AC Compressor condenser price is crucial for automakers aiming to balance performance with affordability without sacrificing quality or reliability. When evaluating options like central condensers versus compressors within vehicles or fleet management scenarios, companies must also account for potential service costs down the line—highlighting why knowing about air compressor condensers is key when planning budgets for new models or replacements.
Cost Comparisons

When it comes to cooling systems, understanding the financial implications of choosing between an air conditioner condenser and compressor is crucial. The costs associated with these components can vary significantly, impacting both initial investments and long-term maintenance expenses. This section will break down the pricing structures of AC systems, focusing on the differences between condensers and compressors.
AC Compressor Condenser Price Breakdown
The price of an AC compressor condenser can fluctuate based on several factors including brand, efficiency rating, and size. Typically, you might find that a basic air conditioner condenser vs compressor setup ranges from $1,000 to $4,000 for complete systems. However, high-efficiency models or those designed for larger spaces can push this price even higher, making it essential to consider your specific needs when budgeting.
Additionally, installation costs can also add a significant amount to your overall expenditure. While some may attempt DIY installations to save money, hiring professionals is often recommended for optimal performance and safety. Understanding these costs helps in making informed decisions when comparing central condenser vs compressor options.
Expenses Related to Replacement Costs
Replacement costs are another critical aspect when discussing air compressor condenser longevity and efficiency. The average lifespan of an AC system can range from 10-15 years; however, components like compressors may need replacement sooner due to wear and tear or mechanical failure. When considering replacement costs for an AC compressor and condenser setup, you should expect anywhere from $800 to $2,500 depending on the specific part needed.
Moreover, if you're facing issues with either component—compressor vs condenser vs evaporator—the expenses can quickly add up if multiple parts require attention simultaneously. Regular maintenance can extend the life of these components but be prepared for occasional replacements as part of owning any cooling system.
Central Condenser vs Compressor: A Financial View
From a financial perspective, comparing central condensers versus compressors reveals distinct cost benefits depending on usage scenarios and system requirements. Generally speaking, central condensers are more efficient in larger homes but come with higher upfront costs while compressors may offer more flexibility in smaller setups at a lower initial price point.
However, it's essential to look beyond just initial investments; operational efficiency plays a crucial role in long-term savings on energy bills as well as maintenance expenses over time—making it imperative to weigh all factors carefully before deciding between an air conditioner condenser vs compressor setup.
In conclusion, understanding the cost comparisons between these two vital components will help ensure that you make a choice that aligns with both your budgetary constraints and cooling needs effectively.
Maintenance and Longevity

When it comes to keeping your cooling systems running smoothly, maintenance is key. Understanding the differences between an air conditioner condenser vs compressor can help you prioritize care for each component. Regular upkeep not only extends the lifespan of these parts but also enhances overall system efficiency.
Tips for Long-lasting Compressors
To ensure your compressor remains in peak condition, regular inspections are essential. Keep an eye on refrigerant levels, as low levels can strain the compressor and lead to costly repairs down the line—think AC compressor and condenser replacement cost. Additionally, investing in a quality filter can prevent dirt buildup, which is crucial since a dirty filter can cause overheating and inefficiency.
Another tip is to maintain proper airflow around your unit; this aids in cooling and reduces wear on the motor. Ensuring that areas around your compressor are free from debris will enhance its performance—after all, no one wants to deal with a central condenser vs compressor debate when their system fails unexpectedly! Lastly, consider scheduling professional maintenance at least once a year to catch any potential issues before they escalate.
Caring for Your Air Conditioner Condenser
Just like its counterpart, the air conditioner condenser requires specific attention to function optimally. Start by cleaning the coils regularly; dirt accumulation can significantly hinder performance and increase energy costs—nobody enjoys high AC Compressor condenser price tags! Using a soft brush or vacuum can help remove debris without damaging delicate components.
Additionally, check for any signs of corrosion or rust on the exterior of your condenser unit. Addressing minor issues promptly can prevent major problems later on—like those pesky replacement costs we discussed earlier! Lastly, ensure that vegetation around your outdoor unit is trimmed back; plants should be kept at least two feet away from the unit for optimal airflow.
Understanding Signs of Wear and Tear
Recognizing signs of wear and tear early on can save you from extensive repairs or replacements later—a lesson learned by many who have faced the dreaded air compressor condenser failure! Listen for unusual noises such as grinding or hissing; these sounds could indicate internal damage that needs immediate attention. Additionally, if you notice decreased cooling efficiency or increased energy bills without any changes in usage patterns, it may be time to investigate further.
Visual cues are also important: leaks around either component may point toward serious issues requiring professional evaluation—such as deciding between central condenser vs compressor options based on severity! Keeping an eye out for these indicators ensures that you maintain both components effectively while avoiding unnecessary headaches down the road.
Conclusion

In the realm of cooling solutions, understanding the distinctions between an air conditioner condenser and a compressor is crucial for making an informed decision. As we’ve explored throughout this guide, each component plays a vital role in HVAC systems, with unique functionalities that cater to various needs. The choice between these systems can significantly impact efficiency, cost, and overall performance.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
When selecting between a condenser vs compressor setup, consider your specific cooling requirements and operational environment. For instance, residential spaces may benefit more from an air conditioner condenser due to its efficient heat exchange capabilities, while industrial applications might lean towards robust compressors for heavy-duty tasks. Evaluating factors such as size, energy efficiency ratings, and installation costs—including AC compressor condenser price—will help you make the best choice tailored to your needs.
Understanding Overall System Efficiency
Efficiency is paramount when comparing central condenser vs compressor systems; it affects not only energy consumption but also your utility bills over time. An efficient air compressor condenser can significantly reduce environmental impact while providing optimal cooling performance. Understanding how each unit operates—particularly in relation to their counterparts like evaporators—will aid in maximizing system efficiency and prolonging equipment life.
Future Trends in Cooling Solutions with ARCTIC
As technology advances, we see exciting trends emerging in cooling solutions that promise enhanced efficiency and sustainability; ARCTIC is at the forefront of this evolution. Innovations such as smart sensors and eco-friendly refrigerants are set to redefine how we approach the age-old debate of compressor vs condenser vs evaporator configurations. Keeping an eye on these developments will ensure you stay ahead of the curve while making informed decisions about AC compressor and condenser replacement costs down the line.
